ADP-ribosylation factor 6 and endocytosis at the apical surface of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells
- PMID: 10508850
- PMCID: PMC2164974
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.147.1.7
ADP-ribosylation factor 6 and endocytosis at the apical surface of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells
Abstract
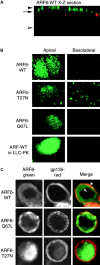
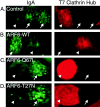
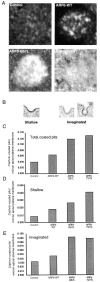
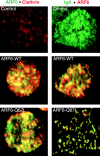
We report that the small GTPase, ADP-ribosylation factor 6 (ARF6), is present only on the apical surface of polarized MDCK epithelial cells. Overexpression of a mutant of ARF6, ARF6-Q67L, which is predicted to be in the GTP-bound form, stimulates endocytosis exclusively at this surface. Surprisingly, overexpression of the mutant ARF6-T27N, which is predicted to be in the GDP-bound form, also stimulated apical endocytosis, though to a lesser extent. ARF6-stimulated endocytosis is inhibited by a dominant-negative form of dynamin, or a dominant-negative hub fragment of clathrin heavy chain, indicating that it is mediated by clathrin. Correspondingly, overexpression of either mutant of ARF6 leads to an increase in the number of clathrin-coated pits at the apical plasma membrane. When ARF6-Q67L is overexpressed in the presence of the dominant-negative dynamin, the ARF6-Q67L colocalizes with clathrin and with IgA bound to its receptor. We conclude that ARF6 is an important modulator of clathrin-mediated endocytosis at the apical surface of epithelial cells.
Figures

References
-
- Apodaca G., Aroeti B., Tang K., Mostov K.E. Brefeldin-A inhibits the delivery of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor to the basolateral surface of MDCK cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:20380–20385. - PubMed
-
- Boman A.L., Kahn R.A. Arf proteinsthe membrane traffic police? Trends Biochem. Sci. 1995;20:147–150. - PubMed
-
- Cavenaugh M.M., Whitney J.A., Carroll K., Zhang C.-J., Boman A.L., Rosenwald A.G., Mellman I., Kahn R.A. Intracellular distribution of Arf proteins in mammalian cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:21767–21774. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

