The influence of frusemide formulation on diuretic effect and efficiency
- PMID: 10510147
- PMCID: PMC2014321
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1999.00015.x
The influence of frusemide formulation on diuretic effect and efficiency
Abstract
Aims: Changes in drug delivery rate may result in clinically important changes in drug effects. For the loop diuretic frusemide, it would be desirable to develop controlled release preparations, that could maintain an effective urinary excretion rate over a prolonged period of time. The aim of this study was to investigate the influence of frusemide formulation on frusemide recovery, diuretic effect and efficiency.
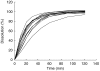
Methods: Twelve subjects were given 60 mg of four different frusemide controlled release formulations in a single-dose, double-blind, randomized 4-way cross-over design. The formulations were three study drugs with different extended dissolution rates (ER1Tab, ER2Tab and ER3Caps ) and one reference drug (LR). Urinary volume and contents of frusemide in urine were measured in samples collected over 24 h.
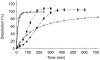
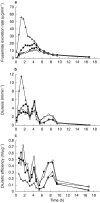
Results: Substantial differences in frusemide recovery and diuretic efficiency were observed between LR and all other formulations. At 24 h, mean total frusemide recoveries of ER1Tab, ER2Tab and ER3Caps were 52%, 36% and 57% lower, respectively, compared with LR (P<0.01). Also at 24 h, mean total diuretic efficiency for ER1Tab, ER2Tab and ER3Caps was 83%, 31% and 135% higher, respectively, compared to LR. The rapid dissolution and absorption of LR resulted in a high diuretic response from 0 to 3 h after dosing. However, from 0 to 24 h, there were no differences in diuretic response between the formulations.
Conclusions: Controlled release formulations of frusemide with a low and extended rate of dissolution lead to a more prolonged absorption and subsequent diuresis, but still maintain a similar cumulative response, due to their higher diuretic efficiency.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discrepancy between bioavailability as estimated from urinary recovery of frusemide and total diuretic effect.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1992 Jul;34(1):47-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1992.tb04106.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1992. PMID: 1633067 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Diuretic effect and diuretic efficiency after intravenous dosage of frusemide.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;29(2):215-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1990.tb03622.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1990. PMID: 2306413 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of drug input rate on the development of tolerance to frusemide.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1998 Nov;46(5):479-87. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1998.00802.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9833602 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical pharmacology of furosemide in children: a supplement.Am J Ther. 2001 Jul-Aug;8(4):275-89. doi: 10.1097/00045391-200107000-00010. Am J Ther. 2001. PMID: 11441327 Review.
-
Clinical consequences of the biphasic elimination kinetics for the diuretic effect of furosemide and its acyl glucuronide in humans.J Pharm Pharmacol. 1999 Mar;51(3):239-48. doi: 10.1211/0022357991772402. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10344623 Review.
Cited by
-
Sodium and Fluid Excretion With Torsemide in Healthy Subjects is Limited by the Short Duration of Diuretic Action.J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Oct 5;6(10):e006135. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.006135. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28982672 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized, open-label, blinded-endpoint, crossover, single-dose study to compare the pharmacodynamics of torasemide-PR 10 mg, torasemide-IR 10 mg, and furosemide-IR 40 mg, in patients with chronic heart failure.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Aug 5;9:4291-302. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S86300. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26273191 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Banerjee PS, Robinson JR. Novel drug delivery systems: an overview of their impact on clinical pharmacokinetic studies. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1991;20:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Kaojarern S, Day B, Brater DC. The time course of delivery of furosemide into urine: an independent determinant of overall response. Kidney Int. 1982;22:69–74. - PubMed
-
- van Meyel JJ, Smits P, Russel FG, Gerlag PG, Tan Y, Gribnau FW. Diuretic efficiency of furosemide during continuous administration versus bolus injection in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1992;51:440–444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

