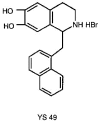
Prevention of the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase by a novel positive inotropic agent, YS 49, in rat vascular smooth muscle and RAW 264.7 macrophages
- PMID: 10510445
- PMCID: PMC1571637
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702787
Prevention of the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase by a novel positive inotropic agent, YS 49, in rat vascular smooth muscle and RAW 264.7 macrophages
Abstract
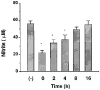
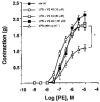
1 The effects of a novel positive inotropic isoquinoline compound, YS 49, on NO production and iNOS protein expression were investigated in cultured rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cells (RAVSMC) and RAW 264.7 cells exposed to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) plus interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). In addition, the effects of YS 49 on vascular hyporeactivity in vitro and ex vivo, and on survival rate (mice) and serum NOx (rat) levels, were also investigated in LPS-treated animals. 2 Pre- or co-treatment of YS 49 with LPS plus IFN-gamma, concentration-dependently reduced NO production in RAVSMC and RAW 264.7 cells (IC50 values, 22 and 30 microM, respectively). Although the inhibitory effect on NO production was reduced when YS 49 was applied 2 and 4 h after cytokine in RAW 264.7 cells, it was still statistically significant (P<0.05). 3 YS 49 reduced iNOS mRNA expression in LPS-treated rat aorta in vitro, an effect which was associated with restoration of contractility to the vasoconstrictor, phenylephrine (PE), and reduction in L-arginine-induced relaxation. 4 Serum NOx levels were significantly (P<0.01) reduced by YS 49 (5 mg kg-1, i.p.) in LPS-treated rats (10 mg kg-1, i.p.). Administration of YS 49 (10 and 20 mg kg-1) 30 min prior to LPS (10 mg kg-1) also significantly (P<0.01) increased the subsequent survival rates in mice. 5 Finally, expression of iNOS protein induced by LPS plus IFN-gamma in RAVSMC and RAW 264.7 cells was suppressed by YS 49, in a concentration-dependent manner. 6 These data strongly suggest that YS 49 suppresses iNOS gene expression induced by LPS and/or cytokines in RAVSMC and RAW 264.7 cells at the transcriptional level. YS 49 could therefore be beneficial in septic shock and other diseases associated with iNOS over-expression.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Inhibition of activation of nuclear factor kappaB is responsible for inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by higenamine, an active component of aconite root.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Oct;291(1):314-20. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999. PMID: 10490919
-
A synthetic isoquinoline alkaloid, 1-(beta-naphthylmethyl)-6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline (YS 51), reduces inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and improves survival in a rodent model of endotoxic shock.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002 May;301(2):561-7. doi: 10.1124/jpet.301.2.561. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002. PMID: 11961057
-
Interleukin-13 is a more potent inhibitor of the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in smooth muscle cells than in macrophages: a comparison with interleukin-4 and interleukin-10.Shock. 1997 Dec;8(6):409-14. Shock. 1997. PMID: 9421853
-
Suppression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression by THI 52, a new synthetic naphthyl-benzylisoquinoline alkaloid.Biochem Pharmacol. 2003 Feb 1;65(3):457-64. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(02)01549-6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12527339
-
Ergolide, sesquiterpene lactone from Inula britannica, inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclo-oxygenase-2 expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages through the inactivation of NF-kappaB.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Jun;133(4):503-12. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704099. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11399667 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Metformin inhibits HMGB1 release in LPS-treated RAW 264.7 cells and increases survival rate of endotoxaemic mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Apr;162(7):1498-508. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01126.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21091653 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of PPAR-gamma by carbon monoxide from CORM-2 leads to the inhibition of iNOS but not COX-2 expression in LPS-stimulated macrophages.Inflammation. 2009 Dec;32(6):364-71. doi: 10.1007/s10753-009-9144-0. Inflammation. 2009. PMID: 19705266
-
CKD-712, (S)-1-(α-naphthylmethyl)-6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline, Inhibits the NF-κB Activation and Augments Akt Activation during TLR4 Signaling.Immune Netw. 2011 Dec;11(6):420-3. doi: 10.4110/in.2011.11.6.420. Epub 2011 Dec 31. Immune Netw. 2011. PMID: 22346785 Free PMC article.
-
The heme oxygenase-1 inducer THI-56 negatively regulates iNOS expression and HMGB1 release in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells and CLP-induced septic mice.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 3;8(10):e76293. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076293. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24098466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BOUMA M.G., STAD R.K., VAN DEN WILDENBERG F.A., BUURMAN W.A. Differential regulatory effects of adenosine on cytokine release by activated human monocytes. J. Immunol. 1994;153:4159–4168. - PubMed
-
- BUSSE R., MULSCH A. Induction of nitric oxide synthase by cytokines in vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1990;275:87–90. - PubMed
-
- CHANG K.C., CHUNG S.Y., CHONG W.S., SUH J.S., KIM S.H., NOH H.K., SEONG B.W., KO H.J., CHUN K.W. Possible superoxide radical-induced alteration of vascular reactivity in aortas from streptozotocin-treated rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1993a;266:992–1000. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

