Kinesin-II is preferentially targeted to assembling cilia and is required for ciliogenesis and normal cytokinesis in Tetrahymena
- PMID: 10512852
- PMCID: PMC25561
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.10.3081
Kinesin-II is preferentially targeted to assembling cilia and is required for ciliogenesis and normal cytokinesis in Tetrahymena
Abstract
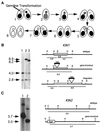
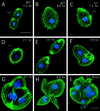
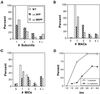
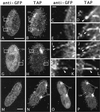
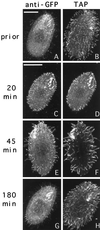
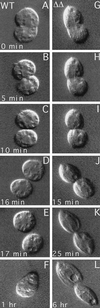
We cloned two genes, KIN1 and KIN2, encoding kinesin-II homologues from the ciliate Tetrahymena thermophila and constructed strains lacking either KIN1 or KIN2 or both genes. Cells with a single disruption of either gene showed partly overlapping sets of defects in cell growth, motility, ciliary assembly, and thermoresistance. Deletion of both genes resulted in loss of cilia and arrests in cytokinesis. Mutant cells were unable to assemble new cilia or to maintain preexisting cilia. Double knockout cells were not viable on a standard medium but could be grown on a modified medium on which growth does not depend on phagocytosis. Double knockout cells could be rescued by transformation with a gene encoding an epitope-tagged Kin1p. In growing cells, epitope-tagged Kin1p preferentially accumulated in cilia undergoing active assembly. Kin1p was also detected in the cell body but did not show any association with the cleavage furrow. The cell division arrests observed in kinesin-II knockout cells appear to be induced by the loss of cilia and resulting cell paralysis.
Figures



References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Sequence homology searches done using BLAST. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Bre M-H, et al. Axonemal tubulin polyglycylation probed with two monoclonal antibodies: widespread evolutionary distribution, appearance during spermatozoan maturation and possible function in motility. J Cell Sci. 1996;109:727–738. - PubMed
-
- Callen A-M, et al. Isolation and characterization of libraries of monoclonal antibodies directed against various forms of tubulin in Paramecium. Biol Cell. 1994;81:95–119. - PubMed
-
- Calzone FJ, Gorovsky MA. Cilia regeneration in Tetrahymena. Exp Cell Res. 1982;140:474–476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

