Activation of pancreatic stellate cells in human and experimental pancreatic fibrosis
- PMID: 10514391
- PMCID: PMC1867025
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65211-X
Activation of pancreatic stellate cells in human and experimental pancreatic fibrosis
Abstract
The mechanisms of pancreatic fibrosis are poorly understood. In the liver, stellate cells play an important role in fibrogenesis. Similar cells have recently been isolated from the pancreas and are termed pancreatic stellate cells. The aim of this study was to determine whether pancreatic stellate cell activation occurs during experimental and human pancreatic fibrosis. Pancreatic fibrosis was induced in rats (n = 24) by infusion of trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) into the pancreatic duct. Surgical specimens were obtained from patients with chronic pancreatitis (n = 6). Pancreatic fibrosis was assessed using the Sirius Red stain and immunohistochemistry for collagen type I. Pancreatic stellate cell activation was assessed by staining for alpha-smooth muscle actin (alphaSMA), desmin, and platelet-derived growth factor receptor type beta (PDGFRbeta). The relationship of fibrosis to stellate cell activation was studied by staining of serial sections for alphaSMA, desmin, PDGFRbeta, and collagen, and by dual-staining for alphaSMA plus either Sirius Red or in situ hybridization for procollagen alpha(1) (I) mRNA. The cellular source of TGFbeta was examined by immunohistochemistry. The histological appearances in the TNBS model resembled those found in human chronic pancreatitis. Areas of pancreatic fibrosis stained positively for Sirius Red and collagen type I. Sirius Red staining was associated with alphaSMA-positive cells. alphaSMA staining colocalized with procollagen alpha(1) (I) mRNA expression. In the rat model, desmin staining was associated with PDGFRbeta in areas of fibrosis. TGFbeta was maximal in acinar cells adjacent to areas of fibrosis and spindle cells within fibrotic bands. Pancreatic stellate cell activation is associated with fibrosis in both human pancreas and in an animal model. These cells appear to play an important role in pancreatic fibrogenesis.
Figures

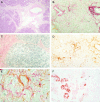
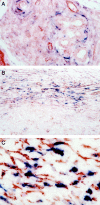
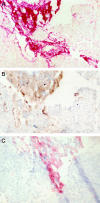
References
-
- Ahern M, Hall P, Halliday, Liddle C, Olynyk J, Ramm G, Denk H: Hepatic stellate cell nomenclature (letter). Hepatology 1996, 23:193. - PubMed
-
- Friedman SD: The cellular basis of hepatic fibrosis. N Engl J Med 1993, 328:1828-1835 - PubMed
-
- Friedman SL: Cellular sources of collagen and regulation of collagen production in liver. Semin Liver Dis 1990, 10:20-29 - PubMed
-
- Yokoi Y, Namihisa T, Kuroda H, Komatsu I, Miyazaki A, Watanabe S, Usui K: Immunocytochemical detection of desmin in fat-storing cells (Ito cells). Hepatology 1984, 4:709-714 - PubMed
-
- Friedman SL, Yamasaki G, Wong L: Modulation of transforming growth factor beta receptors of rat lipocytes during the hepatic wound healing response: enhanced binding and reduced gene expression accompany cellular activation in culture and in vivo. J Biol Chem 1994, 269:10551-10558 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

