Ferric enterochelin transport in Yersinia enterocolitica: molecular and evolutionary aspects
- PMID: 10515929
- PMCID: PMC103774
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.20.6387-6395.1999
Ferric enterochelin transport in Yersinia enterocolitica: molecular and evolutionary aspects
Abstract
Yersinia enterocolitica is well equipped for siderophore piracy, encompassing the utilization of siderophores such as ferrioxamine, ferrichrome, and ferrienterochelin. In this study, we report on the molecular and functional characterization of the Yersinia fep-fes gene cluster orthologous to the Escherichia coli ferrienterochelin transport genes (fepA, fepDGC, and fepB) and the esterase gene fes. In vitro transcription-translation analysis identified polypeptides of 30 and 35 kDa encoded by fepC and fes, respectively. A frameshift mutation within the fepA gene led to expression of a truncated polypeptide of 40 kDa. The fepD, fepG, and fes genes of Y. enterocolitica were shown to complement corresponding E. coli mutants. Insertional mutagenesis of fepD or fes genes abrogates enterochelin-supported growth of Y. enterocolitica on iron-chelated media. In contrast to E. coli, the fep-fes gene cluster in Y. enterocolitica consists solely of genes required for uptake and utilization of enterochelin (fep) and not of enterochelin synthesis genes such as entF. By Southern hybridization, fepDGC and fes sequences could be detected in Y. enterocolitica biotypes IB, IA, and II but not in biotype IV strains, Yersinia pestis, and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis strains. According to sequence alignment data and the coherent structure of the Yersinia fep-fes gene cluster, we suggest early genetic divergence of ferrienterochelin uptake determinants among species of the family Enterobacteriaceae.
Figures


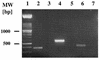
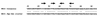
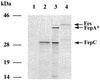
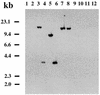
Similar articles
-
The yersiniabactin biosynthetic gene cluster of Yersinia enterocolitica: organization and siderophore-dependent regulation.J Bacteriol. 1998 Feb;180(3):538-46. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.3.538-546.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9457855 Free PMC article.
-
A lipoprotein of Yersinia enterocolitica facilitates ferrioxamine uptake in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):1029-35. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.1029-1035.1992. J Bacteriol. 1992. PMID: 1732192 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic organization of multiple fep genes encoding ferric enterobactin transport functions in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3638-46. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3638-3646.1987. J Bacteriol. 1987. PMID: 2956250 Free PMC article.
-
The TonB protein of Yersinia enterocolitica and its interactions with TonB-box proteins.Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Feb;237(1-2):152-60. doi: 10.1007/BF00282796. Mol Gen Genet. 1993. PMID: 8384290
-
Hunger for iron: the alternative siderophore iron scavenging systems in highly virulent Yersinia.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012 Nov 30;2:151. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00151. eCollection 2012. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23226687 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pseudomonas fluorescens pirates both ferrioxamine and ferricoelichelin siderophores from Streptomyces ambofaciens.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 May 1;81(9):3132-41. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03520-14. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25724953 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer of the core region genes of the Yersinia enterocolitica WA-C serotype O:8 high-pathogenicity island to Y. enterocolitica MRS40, a strain with low levels of pathogenicity, confers a yersiniabactin biosynthesis phenotype and enhanced mouse virulence.Infect Immun. 2002 Apr;70(4):1832-41. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.4.1832-1841.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 11895945 Free PMC article.
-
The BfeR regulator mediates enterobactin-inducible expression of Bordetella enterobactin utilization genes.J Bacteriol. 2004 Nov;186(21):7302-11. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.21.7302-7311.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15489442 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the expression of the Vibrio parahaemolyticus peuA gene encoding an alternative ferric enterobactin receptor.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 22;9(8):e105749. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105749. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25148374 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Analysis of Yersinia enterocolitica Biovar 1B Infecting Murine Macrophages Reveals New Mechanisms of Extracellular and Intracellular Survival.Infect Immun. 2015 Jul;83(7):2672-85. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02922-14. Epub 2015 Apr 20. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 25895974 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 1989.
-
- Bäumler A J, Koebnik R, Stojiljkovic I, Heesemann J, Braun V, Hantke K. Survey on newly characterized iron uptake systems of Yersinia enterocolitica. Zentbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1993;278:416–424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

