Functional characterization of a Na+-phosphate cotransporter (NaPi-II) from zebrafish and identification of related transcripts
- PMID: 10517802
- PMCID: PMC2269579
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.00079.x
Functional characterization of a Na+-phosphate cotransporter (NaPi-II) from zebrafish and identification of related transcripts
Abstract
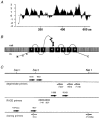
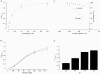
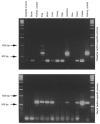
1. We report the molecular identification of a Na+-Pi (inorganic phosphate) cotransport system of the NaPi-II protein family from zebrafish intestine. Following a PCR-related strategy, a DNA fragment from intestine-derived RNA was isolated. Rapid amplification of cDNA ends (3'- and 5'-RACE) resulted in the complete sequence (2607 bp) containing an open reading frame of 1893 bp. 2. The NaPi-II-related protein was expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes and the resulting transport activity was analysed by electrophysiological means. The apparent Km for Pi was 250 microM (96 mM Na+, -60 mV), and voltage-dependent binding of Na+ exhibited a Km of 67.1 mM (1 mM Pi, -60 mV). 3. Interestingly, the overall transport activity was almost insensitive to changes in the holding potential. The apparent affinity for Na+ decreased under hyperpolarizing conditions, whereas Pi binding showed no voltage dependence. Transport activity was inhibited at low pH, which is characteristic for renal NaPi-II isoforms. 4. The expression of the NaPi-II-related isoform was addressed by reverse-transcription PCR. The mRNA could be detected in intestine, liver, eye and kidney. Unexpectedly, a second NaPi-II-related isoform was identified and found to be expressed in kidney, intestine, liver, brain, eye and prominently in testis. In addition, a shorter amplicon was demonstrated to be an antisense transcript related to the NaPi-II intestinal isoform.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of a type IIb sodium-phosphate cotransporter from zebrafish (Danio rerio) kidney.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003 Apr;284(4):F727-36. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00356.2002. Epub 2002 Dec 17. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12488247
-
Cloning and expression of a renal Na-Pi cotransport system from flounder.Am J Physiol. 1994 Aug;267(2 Pt 2):F311-7. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.267.2.F311. Am J Physiol. 1994. PMID: 8067391
-
Cloning of a rabbit renal Na-Pi cotransporter, which is regulated by dietary phosphate.Am J Physiol. 1995 Apr;268(4 Pt 2):F626-33. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1995.268.4.F626. Am J Physiol. 1995. PMID: 7733319
-
Regulation of the NPT gene by a naturally occurring antisense transcript.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2002;36(2-3):241-52. doi: 10.1385/CBB:36:2-3:241. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2002. PMID: 12139410 Review.
-
Evolution of the Na-P(i) cotransport systems.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001 Feb;280(2):R301-12. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.2001.280.2.R301. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11208556 Review.
Cited by
-
Significant Variations in Double-Stranded RNA Levels in Cultured Skin Cells.Cells. 2024 Jan 25;13(3):226. doi: 10.3390/cells13030226. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38334619 Free PMC article.
-
Electrogenic kinetics of a mammalian intestinal type IIb Na(+)/P(i) cotransporter.J Membr Biol. 2006;212(3):177-90. doi: 10.1007/s00232-006-0016-3. Epub 2007 Mar 6. J Membr Biol. 2006. PMID: 17342377
-
Type II Na+-phosphate Cotransporters and Phosphate Balance in Teleost Fish.Pflugers Arch. 2019 Jan;471(1):193-212. doi: 10.1007/s00424-018-2239-4. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Pflugers Arch. 2019. PMID: 30542786 Review.
-
Physiological and molecular mechanisms of inorganic phosphate handling in the toad Bufo bufo.Pflugers Arch. 2007 Apr;454(1):101-13. doi: 10.1007/s00424-006-0176-0. Epub 2006 Dec 13. Pflugers Arch. 2007. PMID: 17165072
-
Strand selective generation of endo-siRNAs from the Na/phosphate transporter gene Slc34a1 in murine tissues.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Apr;37(7):2274-82. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp088. Epub 2009 Feb 23. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19237395 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berndt TJ, Knox FG. Renal regulation of phosphate excretion. In: Seldin DW, Giebisch G, editors. The Kidney: Physiology and Pathophysiology. New York: Raven Press; 1992. pp. 2511–2532.
-
- Busch AE, Biber J, Murer H, Lang F. Electrophysiological insights of type I and II Na/Pi transporters. Kidney International. 1996;49:986–987. - PubMed
-
- Busch AE, Wagner CA, Schuster A, Waldegger S, Biber J, Murer H, Lang F. Properties of electrogenic Pi transport by a human renal brush border Na+/Pi transporter. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 1995;6:1547–1551. - PubMed
-
- Busch A, Waldegger S, Herzer T, Biber J, Markovich D, Hayes G, Murer H, Lang F. Electrophysiological analysis of Na+/Pi cotransport mediated by a transporter cloned from rat kidney and expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA. 1994;91:8205–8208. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

