Effect of renal perfusion pressure on renal function, renin release and renin and angiotensinogen gene expression in rats
- PMID: 10517817
- PMCID: PMC2269577
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.t01-1-00261.x
Effect of renal perfusion pressure on renal function, renin release and renin and angiotensinogen gene expression in rats
Abstract
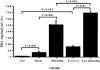
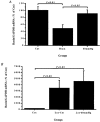
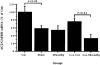
1. A study was undertaken to examine the influence of acute renal perfusion pressure (RPP) reduction on renin release, renal renin and angiotensinogen gene expression and the role played by angiotensin II in these responses. 2. In chloralose-urethane anaesthetised rats, reduction of RPP to 60 mmHg for 3 h in vehicle or losartan-treated (5 days at 10 mg kg-1 bis in die (b.i.d.)) rats decreased renal blood flow by 46 and 29 % (both P < 0.001), respectively, glomerular filtration rate by 45 and 57 % (both P < 0.001), respectively, and sodium excretion by 96 and 98 % (both P < 0.01). 3. Chloralose-urethane anaesthesia and surgery caused a rise in plasma renin activity but was associated with a suppression of renal renin (50 %, P < 0.01) and angiotensinogen (40 %, P < 0.05) gene expression. Following reduction of RPP to 60 mmHg for 3 h, plasma renin activity was increased more than 7-fold (P < 0.001) and renal renin gene expression about 2-fold (P < 0.05). 4. Chronic (5 days) blockade of angiotensin II receptors with losartan elevated plasma renin activity some 29-fold (P < 0.001) and caused a marked increase (30-fold, P < 0.05) in renal renin gene expression, compatible with angiotensin II exerting a negative feedback control on renin release and gene expression. Reduction of RPP to 60 mmHg for 3 h in these animals had little effect on renal renin gene expression. 5. From these findings it can be concluded that (a) chloralose-urethane anaesthesia and surgery had a stimulatory effect on renin release but suppressed basal levels of renal renin and angiotensinogen gene expression; (b) acute reduction of RPP for 3 h could stimulate renin gene expression in the renin producing cells; and (c) the negative feedback control of angiotensin II on renin release and synthesis which was evident following chronic losartan treatment was not apparent during short-term reduction of RPP.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of isoprenaline infusion on renal renin and angiotensinogen gene expression in the anaesthetised rat.Exp Physiol. 2003 Mar;88(2):221-7. doi: 10.1113/eph8802490. Exp Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12621527
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and AT1 receptor blockade modify the pressure-natriuresis relationship by additive mechanisms in rats with human renin and angiotensinogen genes.J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999 Aug;10(8):1669-80. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V1081669. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999. PMID: 10446934
-
Reciprocal feedback regulation of kidney angiotensinogen and renin mRNA expressions by angiotensin II.Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 1):E863-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1992.263.5.E863. Am J Physiol. 1992. PMID: 1443118
-
[Molecular mechanisms of nephro-protective action of enalapril in experimental chronic renal failure].Ann Acad Med Stetin. 1999;Suppl 52:1-93. Ann Acad Med Stetin. 1999. PMID: 10589103 Review. Polish.
-
The intrarenal renin-angiotensin system.Semin Nephrol. 1993 Jan;13(1):13-30. Semin Nephrol. 1993. PMID: 8434183 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of renin release via cyclic ADP-ribose-mediated signaling: evidence from mice lacking CD38 gene.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;31(1):44-55. doi: 10.1159/000343348. Epub 2013 Jan 14. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23343681 Free PMC article.
-
Combination Therapy with Losartan and α-Tocopherol in Acute Ureteral Obstruction-Induced Renal Excretory Dysfunction and Acidification Defect.Iran J Med Sci. 2014 Jul;39(4):357-66. Iran J Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 25031488 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelium-derived nitric oxide supports renin cell recruitment through the nitric oxide-sensitive guanylate cyclase pathway.Hypertension. 2013 Feb;61(2):400-7. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.00221. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Hypertension. 2013. PMID: 23297374 Free PMC article.
-
Renin Feedback Is an Independent Predictor of Outcome in HFpEF.J Pers Med. 2021 May 3;11(5):370. doi: 10.3390/jpm11050370. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34063595 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdi A, Johns EJ. The effect of angiotensin II receptor antagonists on kidney function in two-kidney, two-clip Goldblatt hypertensive rats. European Journal of Pharmacology. 1997;331:185–192. - PubMed
-
- Doughty SE, Ferrier RK, Hillan KJ, Jackson DG. The effects of Zeneca ZD8731, an angiotensin II antagonist, on renin expression by juxtaglomerular cells in the rat: Comparison of protein and mRNA expression as detected by immunohistochemistry and in-situ hybridization. Toxicologic Pathology. 1995;23:256–261. - PubMed
-
- Dzau VJ, Burt DW, Pratt RE. Molecular biology of the renin-angiotensin system. American Journal of Physiology. 1988;255:F563–573. - PubMed
-
- Ehmke H, Berthold H, Just A, Hackenthal E, Kirchheim HR. Acute short-loop feedback inhibition of renin release by angiotensin II does not play a physiological role in the conscious dog. Kidney International. 1996;50:1801.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

