Cloning, expression, and molecular characterization of a small pea gene family regulated by low levels of ultraviolet B radiation and other stresses
- PMID: 10517839
- PMCID: PMC59410
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.121.2.479
Cloning, expression, and molecular characterization of a small pea gene family regulated by low levels of ultraviolet B radiation and other stresses
Abstract
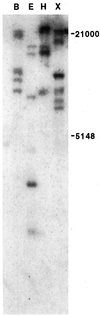
A pea (Pisum sativum) DNA fragment (termed MB3) was isolated by differential display of cDNAs obtained from total leaf RNA of ultraviolet B (UV-B) radiation-treated plants. Longer cDNAs were cloned by rapid amplification of cDNA ends in the 3' to 5' direction. Three different, but very similar, cDNAs were cloned, sadA, sadB, and sadC, the major difference between them being a 36-bp deletion in the coding region of sadB. Southern blotting confirmed the occurrence of at least three genes in the pea genome. Database comparisons of the SAD protein sequences revealed high identity (46%) and similarity (77%) with a putative tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) short-chain alcohol dehydrogenase. Very low levels of UV-B radiation (the biologically effective radiation normalized to 300 nm = 0.08 W m(-2)) was shown to up-regulate expression, a dose considerably lower than that needed to induce expression of the well-known UV-B defensive chalcone synthase and phenylalanine ammonia lyase genes. RNase protection assay revealed that primarily sadA and sadC mRNA accumulation was enhanced by UV-B. In addition to UV-B irradiation, ozone fumigation, wounding, aluminum stress, and salt stress induced increased transcript levels of the sad genes in pea.
Figures

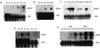

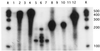

Similar articles
-
Induction of early light-inducible protein gene expression in Pisum sativum after exposure to low levels of UV-B irradiation and other environmental stresses.Plant Cell Rep. 2004 Feb;22(7):532-6. doi: 10.1007/s00299-003-0743-1. Epub 2003 Dec 9. Plant Cell Rep. 2004. PMID: 14663627
-
Regulation of gene expression by low levels of ultraviolet-B radiation in Pisum sativum: isolation of novel genes by suppression subtractive hybridisation.Plant Cell Physiol. 2002 Apr;43(4):402-10. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcf047. Plant Cell Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11978868
-
Identification of a novel nuclear factor-binding site in the Pisum sativum sad gene promoters.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Apr 12;1574(3):231-44. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4781(01)00366-9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 11997088
-
Molecular evolution and functional relevance of the chalcone synthase genes of pea.Mol Gen Genet. 1997 Jun;255(1):28-37. doi: 10.1007/s004380050471. Mol Gen Genet. 1997. PMID: 9230896
-
Radioprotective effect of novel disubstituted thioureas on pea (Pisum sativum L.) development.Radiats Biol Radioecol. 2002 Nov-Dec;42(6):644-53. Radiats Biol Radioecol. 2002. PMID: 12530143 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutation in the putative ketoacyl-ACP reductase CaKR1 induces loss of pungency in Capsicum.Theor Appl Genet. 2019 Jan;132(1):65-80. doi: 10.1007/s00122-018-3195-2. Epub 2018 Sep 28. Theor Appl Genet. 2019. PMID: 30267113
-
Transcriptomic responses to aluminum stress in roots of Arabidopsis thaliana.Mol Genet Genomics. 2008 Apr;279(4):339-57. doi: 10.1007/s00438-007-0316-z. Epub 2008 Feb 13. Mol Genet Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18270741
-
Mesophyll distribution of 'antioxidant' flavonoid glycosides in Ligustrum vulgare leaves under contrasting sunlight irradiance.Ann Bot. 2009 Oct;104(5):853-61. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcp177. Epub 2009 Jul 25. Ann Bot. 2009. PMID: 19633310 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological and transcriptional analysis of the effects of aluminum stress on Cryptococcus humicola.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012 Jun;28(6):2319-29. doi: 10.1007/s11274-012-1039-9. Epub 2012 Mar 17. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22806106
-
Expressed sequence tag-based gene expression analysis under aluminum stress in rye.Plant Physiol. 2002 Dec;130(4):1706-16. doi: 10.1104/pp.009969. Plant Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12481053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belknap WR, Garbarino JE. The role of ubiquitin in plant senescence and stress response. Trends Plant Sci. 1996;1:331–335.
-
- Britt AB, Chen JJ, Wykoff D, Mitchell D. A UV-sensitive mutant of Arabidopsis defective in the repair of pyrimidine-pyrimidinone (6–4) dimers. Science. 1993;264:1571–1574. - PubMed
-
- Brown T. Southern blotting. In: Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore D, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K, editors. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. New York: John Wiley & Son; 1993. pp. 2.9.1–2.9.15.
-
- Caldwell MM. Solar UV irradiation and the growth and development of higher plants. In: Giese AC, editor. Current Topics in Photobiology and Photochemistry. 4: Photophysiology. New York: Academic Press; 1971. pp. 131–177.
-
- Chow WS, Strid Å, Anderson JM. Short-term treatment of pea plants with supplementary ultraviolet-B radiation: recovery time-courses of some photosynthetic functions and components. In: Murata N, editor. Research in Photosynthesis. IV. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1992. pp. 361–364.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

