Biochemical and immunocytochemical characterization of two types of myosins in cultured tobacco bright yellow-2 cells
- PMID: 10517844
- PMCID: PMC59415
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.121.2.525
Biochemical and immunocytochemical characterization of two types of myosins in cultured tobacco bright yellow-2 cells
Abstract
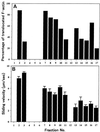
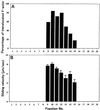
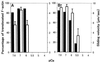
We have isolated a myosin (referred to as 170-kD myosin) from lily pollen tubes, which consists of 170-kD heavy chain and calmodulin (CaM) light chain and is responsible for cytoplasmic streaming. A 170-kD polypeptide that has similar antigenicity to the 170-kD myosin heavy chain of lily pollen tubes was also present in cultured tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) Bright Yellow-2 (BY-2) cells, and possessed the ability to interact with F-actin in an ATP-dependent manner. In addition to this myosin, we identified biochemically another kind of myosin in BY-2 cells. This myosin consisted of a CaM light chain and a 175-kD heavy chain with antigenicity different from the 170-kD myosin heavy chain. In the present study, we referred to this myosin as 175-kD myosin. This myosin was able to translocate rhodamine-phalloidin (RP)-labeled F-actin at an average velocity of about 9 &mgr;m/s in the motility assay in vitro. In contrast, the sliding velocity of RP-labeled F-actin translocated by fractions containing the 170-kD myosin was 3 to 4 &mgr;m/s. The velocity of cytoplasmic streaming in living BY-2 cells ranged from 2 to 9 &mgr;m/s. The motile activity of 175-kD myosin in vitro was inhibited by Ca(2+) at concentrations higher than 10(-6) M. Immunoblot analyses using an antiserum against the heavy chain of 170- or 175-kD myosin revealed that in tobacco plants, the 175-kD myosin was expressed in leaf, stem, and root, but not in germinating pollen, while 170-kD myosin was present in all of these plant parts and in germinating pollen. These results suggest that the two types of myosins, 170 and 175 kD, presumably participate in cytoplasmic streaming in BY-2 cells and other somatic cells of tobacco plants.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Higher plant myosin XI moves processively on actin with 35 nm steps at high velocity.EMBO J. 2003 Mar 17;22(6):1263-72. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg130. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12628919 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory regulation of higher-plant myosin by Ca2+ ions.Plant Physiol. 1999 Jan;119(1):231-40. doi: 10.1104/pp.119.1.231. Plant Physiol. 1999. PMID: 9880365 Free PMC article.
-
Immunochemical and immunocytochemical identification of a myosin heavy chain polypeptide in Nicotiana pollen tubes.J Cell Sci. 1989 Apr;92 ( Pt 4):569-74. doi: 10.1242/jcs.92.4.569. J Cell Sci. 1989. PMID: 2689460
-
Force-velocity relationships in actin-myosin interactions causing cytoplasmic streaming in algal cells.J Exp Biol. 2003 Jun;206(Pt 12):1971-6. doi: 10.1242/jeb.00239. J Exp Biol. 2003. PMID: 12756278 Review.
-
Temperature plasticity of contractile proteins in fish muscle.J Exp Biol. 2002 Aug;205(Pt 15):2231-6. doi: 10.1242/jeb.205.15.2231. J Exp Biol. 2002. PMID: 12110657 Review.
Cited by
-
Myosin-dependent endoplasmic reticulum motility and F-actin organization in plant cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Apr 13;107(15):6894-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911482107. Epub 2010 Mar 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20351265 Free PMC article.
-
Plant-Specific Myosin XI, a Molecular Perspective.Front Plant Sci. 2012 Sep 10;3:211. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00211. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22973289 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of myosin XI genes from the Closterium peracerosum-strigosum-littorale complex and analysis of their expression during sexual reproduction.J Plant Res. 2006 Mar;119(2):105-13. doi: 10.1007/s10265-005-0249-8. Epub 2006 Feb 3. J Plant Res. 2006. PMID: 16456621
-
Higher plant myosin XI moves processively on actin with 35 nm steps at high velocity.EMBO J. 2003 Mar 17;22(6):1263-72. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg130. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12628919 Free PMC article.
-
An isoform of myosin XI is responsible for the translocation of endoplasmic reticulum in tobacco cultured BY-2 cells.J Exp Bot. 2009;60(1):197-212. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ern280. Epub 2008 Nov 27. J Exp Bot. 2009. PMID: 19039101 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Braun M. Immunolocalization of myosin in rhizoids of Chara globularis Thuill. Protoplasma. 1996;191:1–8.
-
- Bush DS. Calcium regulation in plant cells and its role in signaling. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 1995;46:95–122.
-
- Chandra S, Low PS. Measurement of Ca2+ fluxes during elicitation of the oxidative burst in aequorin-transformed tobacco cells. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:28274–28280. - PubMed
-
- Cope MJTV, Whisstock J, Rayment I, Kendrick-Jones J. Conservation within the myosin motor domain: implication for structure and function. Structure. 1996;4:969–987. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

