The clinicopathological features of extensive small intestinal CD4 T cell infiltration
- PMID: 10517900
- PMCID: PMC1727728
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.45.5.662
The clinicopathological features of extensive small intestinal CD4 T cell infiltration
Abstract
Methods: Four patients with clinicopathological features suggesting a new distinct entity defining extensive small intestinal CD4 T cell infiltration were observed.
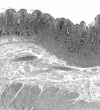
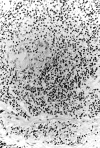
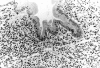
Results: All four patients presented with chronic diarrhoea, malabsorption, and weight loss. Biopsy specimens of the small intestine disclosed extensive and diffuse infiltration of the lamina propria by pleomorphic small T lymphocytes, which were positive for CD3, CD4, CD5, and the beta chain of T cell receptor in all three cases studied and negative for CD103 in all three cases studied. It is notable that, in all invaded areas, the infiltrating cells showed no histological change throughout the whole evolution. In three patients, lymphocyte proliferation was monoclonal and there was extraintestinal involvement. In one patient, lymphoproliferation was oligoclonal and confined to the small intestine. In all four patients, there was no evidence of coeliac disease. Although none of the four patients responded to single or multiple drug chemotherapy, median survival was five years.
Conclusion: Extensive small intestinal CD4 T cell infiltration is a rare entity, distinct from coeliac disease and associated with prolonged survival.
Figures



Comment in
-
T-cell lymphoma: the real thing.Gut. 1999 Nov;45(5):638-9. doi: 10.1136/gut.45.5.638. Gut. 1999. PMID: 10517893 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
