Persistence of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus at very low levels in immune mice
- PMID: 10518559
- PMCID: PMC18395
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.21.11964
Persistence of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus at very low levels in immune mice
Abstract
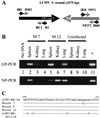
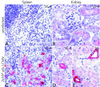
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV), strain WE, is a non-cytopathic RNA virus that is highly adapted to its natural host, the mouse. Acute infection of adult mice leads to generalized virus spread, followed by cytotoxic T lymphocyte-mediated virus clearance below the detection levels of conventional assays within 2-3 weeks. Indirect evidence had suggested that virus or viral antigen might persist in the immune mouse. Here we demonstrate LCMV-WE persistence at low levels after infection with 10(2) or 10(6) plaque-forming units, shown as viral genome, viral antigen, and replicative virus using sensitive in vitro and in vivo assays. The finding that LCMV-WE persists in the face of apparently intact immune responses resembles the situation in some viral (hepatitis B and C, HIV) and bacterial (tuberculosis, leprosy) infections in humans; the results are relevant to the understanding not only of other murine and human persistent viral infections but also of protective immunological memory by "infection immunity."
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

