Decreased selective uptake of high density lipoprotein cholesteryl esters in apolipoprotein E knock-out mice
- PMID: 10518574
- PMCID: PMC18410
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.21.12050
Decreased selective uptake of high density lipoprotein cholesteryl esters in apolipoprotein E knock-out mice
Abstract
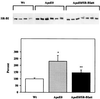
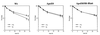
Scavenger receptor BI (SR-BI) mediates the selective uptake of high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesteryl esters (CE) by cells, i.e., the uptake of CE without degradation of HDL protein. Mice with attenuated expression of SR-BI, because of targeted gene mutation (SR-BIatt mice), have increased plasma HDL levels as a result of decreased selective uptake in the liver. To further evaluate the role of SR-BI in lipoprotein metabolism, compound apolipoprotein E knock-out (apoE0)/SR-BIatt mice were bred. Hepatic SR-BI protein was increased (2.3-fold) in apoE0 mice compared with wild type (wt) and was reduced significantly in apoE0/SR-BIatt mice. However, the plasma lipoprotein profile of apoE0 and apoE0/SR-BIatt mice was identical. This was explained by HDL turnover studies that revealed that the selective clearance of HDL CE by the liver and adrenal was already profoundly impaired in apoE0 mice compared with wt (28% of wt in liver). A similar decrease in selective uptake was seen when apoE0 HDL was incubated with isolated apoE0 hepatocytes. The results suggest that apoE plays a major role in the selective clearance of HDL CE by the liver and adrenal gland, possibly by facilitating the presentation of HDL to SR-BI at the cell surface.
Figures


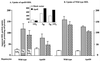
References
-
- Rubin E M, Krauss R M, Spangler E A, Verstuyft J G, Clift S M. Nature (London) 1991;353:265–267. - PubMed
-
- Benoit P, Emmanuel F, Caillaud J M, Bassinet L, Castro G, Gallix P, Fruchart J C, Branellec D, Denefle P, Duverger N. Circulation. 1999;99:105–110. - PubMed
-
- Gordon D J, Rifkind B M. N Engl J Med. 1989;321:1311–1316. - PubMed
-
- Glomset J A. J Lipid Res. 1968;9:155–167. - PubMed
-
- Fielding P E, Miida T, Fielding C J. Biochemistry. 1991;30:8551–8557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

