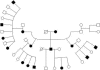
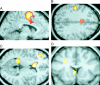
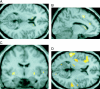
Functional and structural brain abnormalities associated with a genetic disorder of speech and language
- PMID: 10521285
- PMCID: PMC1288272
- DOI: 10.1086/302631
Functional and structural brain abnormalities associated with a genetic disorder of speech and language
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neural basis of an inherited speech and language disorder.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Oct 13;95(21):12695-700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.21.12695. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9770548 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics. First gene linked to speech identified.Science. 2001 Oct 5;294(5540):32. doi: 10.1126/science.294.5540.32a. Science. 2001. PMID: 11588230 No abstract available.
-
Progressive amusia and aprosody.Arch Neurol. 1992 Sep;49(9):971-6. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1992.00530330095023. Arch Neurol. 1992. PMID: 1520089
-
FOXP genes, neural development, speech and language disorders.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009;665:117-29. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-1599-3_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 20429420 Review.
-
Deciphering the genetic basis of speech and language disorders.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2003;26:57-80. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.26.041002.131144. Epub 2003 Jan 8. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12524432 Review.
Cited by
-
FoxP2 expression in avian vocal learners and non-learners.J Neurosci. 2004 Mar 31;24(13):3164-75. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4369-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15056696 Free PMC article.
-
The contribution of theta and delta to feedback processing in children with developmental language disorder.J Neurodev Disord. 2023 Apr 17;15(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s11689-023-09481-1. J Neurodev Disord. 2023. PMID: 37069567 Free PMC article.
-
The pale spear-nosed bat: A neuromolecular and transgenic model for vocal learning.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2022 Nov;1517(1):125-142. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14884. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2022. PMID: 36069117 Free PMC article.
-
CNTNAP2 and language processing in healthy individuals as measured with ERPs.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46995. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046995. Epub 2012 Oct 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23115634 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the genetic foundations of human communication.Neuropsychol Rev. 2015 Mar;25(1):3-26. doi: 10.1007/s11065-014-9277-2. Epub 2015 Jan 18. Neuropsychol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25597031 Review.
References
-
- Aglioti S, Beltramello A, Girardi F, Fabbro F (1996) Neurolinguistic and follow-up study of an unusual pattern of recovery from bilingual subcortical aphasia. Brain 119:1551–1564 - PubMed
-
- Arnold GE (1961) The genetic background of developmental language disorders. Folia Phoniatr 13:246–254 - PubMed
-
- Bishop DV, North T, Donlan C (1995) Genetic basis of specific language impairment: evidence from a twin study. Dev Med Child Neurol 37:56–71 - PubMed
-
- Chi JG, Dooling EC, Gilles FH (1977) Left-right asymmetries of the temporal speech areas of the human fetus. Arch Neurol 34:346–348 - PubMed
-
- Eden GF, VanMeter JW, Rumsey JM, Maisog JM, Woods RP, Zeffiro TA (1996) Abnormal processing of visual motion in dyslexia revealed by functional brain imaging. Nature 382:66–69 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

