Intracellular calcium signals measured with indo-1 in isolated skeletal muscle fibres from control and mdx mice
- PMID: 10523411
- PMCID: PMC2269592
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.00417.x
Intracellular calcium signals measured with indo-1 in isolated skeletal muscle fibres from control and mdx mice
Abstract
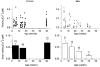
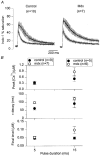
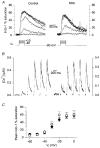
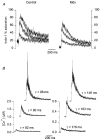
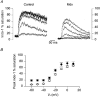
1. Intracellular free calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) was measured with the fluorescent indicator indo-1 in single skeletal fibres enzymatically isolated from the flexor digitorum brevis and interosseus muscles of control and dystrophic mdx C57BL/10 mice. Measurements were taken from a portion of fibre that was voltage clamped to allow detection of depolarization-induced changes in [Ca2+]i. 2. The mean (+/- s.e.m.) initial resting [Ca2+]i from all control and mdx fibres tested was 56 +/- 5 nM (n = 72) and 48 +/- 7 nM (n = 57), respectively, indicating no significant overall difference between the two groups. However, when comparing a batch of control and mdx fibres obtained from mice older than approximately 35 weeks, resting [Ca2+]i was significantly lower in mdx (16 +/- 4 nM, n = 11) than in control fibres (71 +/- 10 nM, n = 14). 3. Changes in [Ca2+]i elicited by short (5-35 ms) depolarizing pulses from -80 to 0 mV showed similar properties in control and mdx fibres. After a 5 ms duration pulse the mean time constant of [Ca2+]i decay was, however, significantly elevated in mdx as compared to control fibres, by a factor of 1.5-2. For longer pulses, no significant difference could be detected. 4. In response to 50 ms duration depolarizing pulses of various amplitudes the threshold for detection of an [Ca2+]i change and the peak [Ca2+]i reached for a given potential were similar in control and mdx fibres. 5. Overall results show that mdx skeletal muscle fibres are quite capable of handling [Ca2+]i at rest and in response to membrane depolarizations.
Figures



References
-
- Anderson JE, Bressler BH, Ovalle WK. Functional regeneration in the hindlimb skeletal muscle of the mdx mouse. Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility. 1988;9:499–515. - PubMed
-
- Berthier C, Amsellem J, Blaineau S. Visualization of the subsarcolemmal cytoskeleton network of mouse skeletal muscle cells by en face views and application to immunoelectron localization of dystrophin. Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility. 1995;16:553–566. - PubMed
-
- Carnwath JW, Shotton DM. Muscular dystrophy in the mdx mouse: histopathology of the soleus and extensor digitorum longus muscles. Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 1987;80:39–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

