Biological and regulatory properties of Vav-3, a new member of the Vav family of oncoproteins
- PMID: 10523675
- PMCID: PMC84867
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.11.7870
Biological and regulatory properties of Vav-3, a new member of the Vav family of oncoproteins
Abstract
We report here the identification and characterization of a novel Vav family member, Vav-3. Signaling experiments demonstrate that Vav-3 participates in pathways activated by protein tyrosine kinases. Vav-3 promotes the exchange of nucleotides on RhoA, on RhoG and, to a lesser extent, on Rac-1. During this reaction, Vav-3 binds physically to the nucleotide-free states of those GTPases. These functions are stimulated by tyrosine phosphorylation in wild-type Vav-3 and become constitutively activated upon deletion of the entire calponin-homology region. Expression of truncated versions of Vav-3 leads to drastic actin relocalization and to the induction of stress fibers, lamellipodia, and membrane ruffles. Moreover, expression of Vav-3 alters cytokinesis, resulting in the formation of binucleated cells. All of these responses need only the expression of the central region of Vav-3 encompassing the Dbl homology (DH), pleckstrin homology (PH), and zinc finger (ZF) domains but do not require the presence of the C-terminal SH3-SH2-SH3 regions. Studies conducted with Vav-3 proteins containing loss-of-function mutations in the DH, PH, and ZF regions indicate that only the DH and ZF regions are essential for Vav-3 biological activity. Finally, we show that one of the functions of the Vav-3 ZF region is to work coordinately with the catalytic DH region to promote both the binding to GTP-hydrolases and their GDP-GTP nucleotide exchange. These results highlight the role of Vav-3 in signaling and cytoskeletal pathways and identify a novel functional cross-talk between the DH and ZF domains of Vav proteins that is imperative for the binding to, and activation of, Rho GTP-binding proteins.
Figures


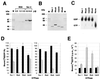


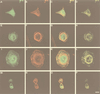

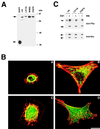

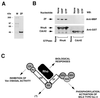
References
-
- Boguski M S, McCormick F. Proteins regulating Ras and its relatives. Nature. 1993;366:643–654. - PubMed
-
- Bustelo X R. The VAV family of signal transduction molecules. Crit Rev Oncog. 1996;7:65–88. - PubMed
-
- Cerione R A, Zheng Y. The Dbl family of oncogenes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996;8:216–222. - PubMed
-
- Coppola J, Bryant S, Koda T, Conway D, Barbacid M. Mechanism of activation of the vav protooncogene. Cell Growth Differ. 1991;2:95–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
