Platelet-activating factor mediates acid-induced lung injury in genetically engineered mice
- PMID: 10525045
- PMCID: PMC481051
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI7727
Platelet-activating factor mediates acid-induced lung injury in genetically engineered mice
Abstract
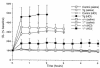
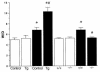
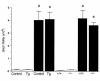
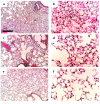
Adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is an acute lung injury of high mortality rate, and the molecular mechanisms underlying it are poorly understood. Acid aspiration-induced lung injury is one of the most common causes of ARDS, characterized by an increase in lung permeability, enhanced polymorphonuclear neutrophil (PMN) sequestration, and respiratory failure. Here, we investigated the role of platelet-activating factor (PAF) and the PAF receptor (PAFR) gene in a murine model of acid aspiration-induced lung injury. Overexpression of the PAFR gene in transgenic mice enhanced lung injury, pulmonary edema, and deterioration of gas exchange caused by HCl aspiration. Conversely, mice carrying a targeted disruption of the PAFR gene experienced significantly less acid-induced injury, edema, and respiratory failure. Nevertheless, the efficiency of PMN sequestration in response to acid aspiration was unaffected by differences in PAFR expression level. The current observations suggest that PAF is involved in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury caused by acid aspiration. Thus, inhibition of this pathway might provide a novel therapeutic approach to acute lung injury, for which no specific pharmaceutical agents are currently available.
Figures



Comment in
-
Two of the usual suspects, platelet-activating factor and its receptor, implicated in acute lung injury.J Clin Invest. 1999 Oct;104(8):1019-20. doi: 10.1172/JCI8506. J Clin Invest. 1999. PMID: 10525039 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Acute lung injury by sepsis and acid aspiration: a key role for cytosolic phospholipase A2.Nat Immunol. 2000 Jul;1(1):42-6. doi: 10.1038/76897. Nat Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10881173
-
Airway hyperresponsiveness in transgenic mice overexpressing platelet activating factor receptor is mediated by an atropine-sensitive pathway.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002 Jan 15;165(2):200-5. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.165.2.2106131. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002. PMID: 11790655
-
Platelet-activating factor plays a pivotal role in the induction of experimental lung injury.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1998 Feb;18(2):197-204. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.18.2.2846. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9476906
-
[Respiratory failure].Nihon Rinsho. 2013 Jun;71(6):1031-4. Nihon Rinsho. 2013. PMID: 23855209 Review. Japanese.
-
Platelet-activating factor (PAF) receptor and genetically engineered PAF receptor mutant mice.Prog Lipid Res. 2000 Jan;39(1):41-82. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7827(99)00016-8. Prog Lipid Res. 2000. PMID: 10729607 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of the platelet-activating factor (PAF) receptor during pulmonary infection with gram negative bacteria.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Nov;137(5):621-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704918. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12381675 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in research on the effects of platelet activation in acute lung injury (Review).Biomed Rep. 2022 Mar;16(3):17. doi: 10.3892/br.2022.1500. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Biomed Rep. 2022. PMID: 35154701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two of the usual suspects, platelet-activating factor and its receptor, implicated in acute lung injury.J Clin Invest. 1999 Oct;104(8):1019-20. doi: 10.1172/JCI8506. J Clin Invest. 1999. PMID: 10525039 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Role of PAF receptors during intestinal ischemia and reperfusion injury. A comparative study between PAF receptor-deficient mice and PAF receptor antagonist treatment.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Jun;139(4):733-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705296. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12812996 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis of oxidized lipid mediators via lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 hydrolysis of extracellular cardiolipin induces endothelial toxicity.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016 Aug 1;311(2):L303-16. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00038.2016. Epub 2016 May 27. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27233995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eijking EP, Gommers D, So KL, Vergeer M, Lachmann B. Surfactant treatment of respiratory failure induced by hydrochloric acid aspiration in rats. Anesthesiology. 1993;78:1145–1151. - PubMed
-
- Goldman G, et al. Reactive oxygen species and elastase mediate lung permeability after acid aspiration. J Appl Physiol. 1992;73:571–575. - PubMed
-
- Pittet JF, Mackersie RC, Martin TR, Matthay MA. Biological markers of acute lung injury: prognostic and pathogenetic significance. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997;155:1187–1205. - PubMed
-
- Prescott SM, Zimmerman GA, McIntyre TM. Platelet-activating factor. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:17381–17384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

