Adenoviral cardiotrophin-1 gene transfer protects pmn mice from progressive motor neuronopathy
- PMID: 10525046
- PMCID: PMC408570
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI6265
Adenoviral cardiotrophin-1 gene transfer protects pmn mice from progressive motor neuronopathy
Abstract
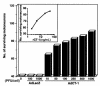
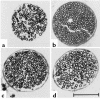
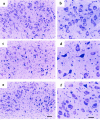
Cardiotrophin-1 (CT-1), an IL-6-related cytokine, causes hypertrophy of cardiac myocytes and has pleiotropic effects on various other cell types, including motoneurons. Here, we analyzed systemic CT-1 effects in progressive motor neuronopathy (pmn) mice that suffer from progressive motoneuronal degeneration, muscle paralysis, and premature death. Administration of an adenoviral CT-1 vector to newborn pmn mice leads to sustained CT-1 expression in the injected muscles and bloodstream, prolonged survival of animals, and improved motor functions. CT-1-treated pmn mice showed a significantly reduced degeneration of facial motoneuron cytons and phrenic nerve myelinated axons. The terminal innervation of skeletal muscle, grossly disturbed in untreated pmn mice, was almost completely preserved in CT-1-treated pmn mice. The remarkable neuroprotection conferred by CT-1 might become clinically relevant if CT-1 side effects, including cardiotoxicity, could be circumvented by a more targeted delivery of this cytokine to the nervous system.
Figures



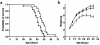
Similar articles
-
In vivo electrotransfer of the cardiotrophin-1 gene into skeletal muscle slows down progression of motor neuron degeneration in pmn mice.Hum Mol Genet. 2002 Jul 1;11(14):1615-25. doi: 10.1093/hmg/11.14.1615. Hum Mol Genet. 2002. PMID: 12075006
-
Adenovirus-mediated transfer of the neurotrophin-3 gene into skeletal muscle of pmn mice: therapeutic effects and mechanisms of action.J Neurol Sci. 1998 Oct;160 Suppl 1:S97-105. doi: 10.1016/s0022-510x(98)00207-x. J Neurol Sci. 1998. PMID: 9851658
-
The effect of the nonpeptide neurotrophic compound SR 57746A on the progression of the disease state of the pmn mouse.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Jun;124(4):811-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701885. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9690875 Free PMC article.
-
Adenoviral gene transfer of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor to injured adult motoneurons.Hum Cell. 2001 Mar;14(1):7-15. Hum Cell. 2001. PMID: 11436355 Review.
-
Cardiotrophin-1: A multifaceted cytokine.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015 Oct;26(5):523-32. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2015.07.009. Epub 2015 Jul 4. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015. PMID: 26188636 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroprotective effects of cardiotrophin-like cytokine on retinal ganglion cells.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2005 Oct;243(10):1036-42. doi: 10.1007/s00417-005-1152-7. Epub 2005 Oct 20. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2005. PMID: 15838664
-
Spinal muscular atrophy disease: a literature review for therapeutic strategies.J Med Life. 2010 Jan-Mar;3(1):3-9. J Med Life. 2010. PMID: 20302191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tetanus toxin C-fragment: the courier and the cure?Toxins (Basel). 2010 Nov;2(11):2622-44. doi: 10.3390/toxins2112622. Epub 2010 Oct 29. Toxins (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22069568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic gene transfer to the nervous system using viral vectors.J Neurovirol. 2003 Apr;9(2):165-72. doi: 10.1080/13550280390193984. J Neurovirol. 2003. PMID: 12707847 Review.
-
Investigation of Galectin-3 and Cardiotrophin-1 Concentrations as Biomarkers in Dogs with Neurological Distemper.Vet Sci. 2025 May 20;12(5):499. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12050499. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40431592 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siddique T, Deng HX. Genetics of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet. 1996;5:1465–1470. - PubMed
-
- Lefebvre S, Burglen L, Frezal J, Munnich A, Melki J. The role of the SMN gene in proximal spinal muscular atrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 1998;7:1531–1536. - PubMed
-
- Thoenen H, Hughes RA, Sendtner M. Trophic support of motoneurons: physiological, pathophysiological, and therapeutic implications. Exp Neurol. 1993;124:47–55. - PubMed
-
- Lindsay RM, Wiegand SJ, Altar CA, DiStefano PS. Neurotrophic factors: from molecule to man. Trends Neurosci. 1994;17:182–190. - PubMed
-
- Henderson CE. Neurotrophic factors as therapeutic agents in ALS. Adv Neurol. 1995;68:235–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

