Cell death of human polymorphonuclear neutrophils induced by a Pseudomonas aeruginosa cystic fibrosis isolate requires a functional type III secretion system
- PMID: 10531282
- PMCID: PMC97008
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.11.6164-6167.1999
Cell death of human polymorphonuclear neutrophils induced by a Pseudomonas aeruginosa cystic fibrosis isolate requires a functional type III secretion system
Abstract
With a coincubation model incorporating Pseudomonas aeruginosa and human polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs), a cystic fibrosis (CF) P. aeruginosa isolate has been shown to resist the bactericidal action of PMNs and to induce their cellular death. An isogenic mutant of this CF isolate in which the type III secretion system was rendered nonfunctional was unable to induce cellular death of PMNs.
Figures
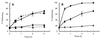
 ) are shown.
) are shown.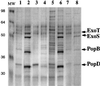
References
-
- Attree, I. Unpublished data.
-
- Coburn J, Wyatt R T, Iglewski B H, Gill D M. Several GTP-binding proteins, including p21c-H-ras, are preferred substrates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:9004–9008. - PubMed
-
- Delic-Attree I, Toussaint B, Froger A, Willison J C, Vignais P M. Isolation of an IHF-deficient mutant of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa mucoid isolate and evaluation of the role of IHF in algD gene expression. Microbiology. 1996;142:2785–2793. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

