Modulation of B-lymphocyte and NK cell activities by glycoinositolphospholipid purified from Trypanosoma cruzi
- PMID: 10531285
- PMCID: PMC97011
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.11.6177-6180.1999
Modulation of B-lymphocyte and NK cell activities by glycoinositolphospholipid purified from Trypanosoma cruzi
Abstract
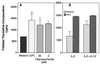
Glycoinositolphospholipids (GIPLs) are some of the major glycolipids of the Trypanosoma cruzi surface that were previously shown to activate B cells. In the present study, we investigated whether (i) T. cruzi GIPLs could induce immunoglobulin secretion from B cells in the absence of T cells and NK cells and whether (ii) NK cells are also stimulated by the GIPLs. B cells purified from mice deficient in both T and NK cells (CD3epsilon transgenic mice) secreted immunoglobulin in response to the GIPL. This response was increased by coculture with a murine NK cell line. The T. cruzi GIPL also increased the NK cell (interleukin-2 induced) proliferative response. Our data indicate that the T. cruzi GIPL has a direct stimulatory effect on NK cells and induces immunoglobulin secretion in the absence of T lymphocytes and NK cells. These findings suggest that this T. cruzi-derived molecule may be one of the stimulators that lead to NK cell activation during T. cruzi infection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Glycoinositolphospholipids from Trypanosoma cruzi induce B cell hyper-responsiveness in vivo.Glycoconj J. 2000 Oct;17(10):727-34. doi: 10.1023/a:1011082925179. Glycoconj J. 2000. PMID: 11425193
-
Glycoinositolphospholipids purified from Trypanosoma cruzi stimulate Ig production in vitro.J Immunol. 1996 Dec 1;157(11):4996-5001. J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8943406
-
Down-regulation of T lymphocyte activation in vitro and in vivo induced by glycoinositolphospholipids from Trypanosoma cruzi. Assignment of the T cell-suppressive determinant to the ceramide domain.J Immunol. 1996 Jan 15;156(2):628-35. J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8543814
-
Glycoinositolphospholipid from Trypanosoma cruzi: structure, biosynthesis and immunobiology.Adv Parasitol. 2004;56:1-41. doi: 10.1016/s0065-308x(03)56001-8. Adv Parasitol. 2004. PMID: 14710995 Review.
-
Glycoinositolphospholipids, free and as anchors of proteins, in Trypanosoma cruzi.Curr Pharm Des. 2001 Aug;7(12):1165-79. doi: 10.2174/1381612013397519. Curr Pharm Des. 2001. PMID: 11472260 Review.
Cited by
-
Glycoinositolphospholipids from Trypanosoma cruzi induce B cell hyper-responsiveness in vivo.Glycoconj J. 2000 Oct;17(10):727-34. doi: 10.1023/a:1011082925179. Glycoconj J. 2000. PMID: 11425193
-
Glycoinositolphospholipids from Trypanosoma cruzi interfere with macrophages and dendritic cell responses.Infect Immun. 2002 Jul;70(7):3736-43. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.7.3736-3743.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12065516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ballas Z D, Rasmussen W L, Krieg A M. Induction of NK activity in murine and human cells by CpG motifs in oligodeoxynucleotides and bacterial DNA. J Immunol. 1996;157:1840–1845. - PubMed
-
- Bento C A M, Melo M B, Previato J O, Mendonça-Previato L, Peçanha L M T. Glycoinositolphospholipids purified from Trypanosoma cruzi stimulate immunoglobulin production in vitro. J Immunol. 1996;157:4996–5001. - PubMed
-
- Bezouska K, Yuen C-T, O'Brien J, Childs R A, Chai W, Lawson A M, Drbal K, Fiserova A, Pospisl M, Feizi T. Oligosaccharide ligands for NKR-P1 protein activate NK cells and cytotoxicity. Nature. 1994;372:150–156. - PubMed
-
- Brunswick M, Finkelman F D, Highet P, Inman J K, Dintzis H M, Mond J J. Picogram quantities of anti-Ig antibodies coupled to dextran induce B cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1988;140:3364–3372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

