Design, synthesis, and biological characterization of a peptide-mimetic antagonist for a tethered-ligand receptor
- PMID: 10535908
- PMCID: PMC22903
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.22.12257
Design, synthesis, and biological characterization of a peptide-mimetic antagonist for a tethered-ligand receptor
Abstract
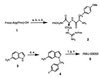
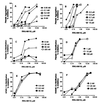
Protease-activated receptors (PARs) represent a unique family of seven-transmembrane G protein-coupled receptors, which are enzymatically cleaved to expose a truncated extracellular N terminus that acts as a tethered activating ligand. PAR-1 is cleaved and activated by the serine protease alpha-thrombin, is expressed in various tissues (e.g., platelets and vascular cells), and is involved in cellular responses associated with hemostasis, proliferation, and tissue injury. We have discovered a series of potent peptide-mimetic antagonists of PAR-1, exemplified by RWJ-56110. Spatial relationships between important functional groups of the PAR-1 agonist peptide epitope SFLLRN were employed to design and synthesize candidate ligands with appropriate groups attached to a rigid molecular scaffold. Prototype RWJ-53052 was identified and optimized via solid-phase parallel synthesis of chemical libraries. RWJ-56110 emerged as a potent, selective PAR-1 antagonist, devoid of PAR-1 agonist and thrombin inhibitory activity. It binds to PAR-1, interferes with PAR-1 calcium mobilization and cellular function (platelet aggregation; cell proliferation), and has no effect on PAR-2, PAR-3, or PAR-4. By flow cytometry, RWJ-56110 was confirmed as a direct inhibitor of PAR-1 activation and internalization, without affecting N-terminal cleavage. At high concentrations of alpha-thrombin, RWJ-56110 fully blocked activation responses in human vascular cells, albeit not in human platelets; whereas, at high concentrations of SFLLRN-NH(2), RWJ-56110 blocked activation responses in both cell types. Thus, thrombin activates human platelets independently of PAR-1, i.e., through PAR-4, which we confirmed by PCR analysis. Selective PAR-1 antagonists, such as RWJ-56110, should serve as useful tools to study PARs and may have therapeutic potential for treating thrombosis and restenosis.
Figures


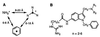


Similar articles
-
Discovery of potent peptide-mimetic antagonists for the human thrombin receptor, protease-activated receptor-1 (PAR-1).Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents. 2003 Mar;1(1):13-36. doi: 10.2174/1568016033356724. Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents. 2003. PMID: 15317288 Review.
-
Peptide-derived protease-activated receptor-1 (PAR-1) antagonists.Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents. 2003 Mar;1(1):1-11. doi: 10.2174/1568016033356689. Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents. 2003. PMID: 15317287 Review.
-
Thrombin receptor (PAR-1) antagonists. Heterocycle-based peptidomimetics of the SFLLR agonist motif.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1998 Jul 7;8(13):1649-54. doi: 10.1016/s0960-894x(98)00292-3. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1998. PMID: 9873407
-
Administration of a potent antagonist of protease-activated receptor-1 (PAR-1) attenuates vascular restenosis following balloon angioplasty in rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001 Jul;298(1):34-42. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001. PMID: 11408522
-
Thrombin receptor antagonists; recent advances in PAR-1 antagonist development.Curr Med Chem. 2002 Jul;9(13):1229-50. doi: 10.2174/0929867023369934. Curr Med Chem. 2002. PMID: 12052165 Review.
Cited by
-
The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2013/14: G protein-coupled receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Dec;170(8):1459-581. doi: 10.1111/bph.12445. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24517644 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation on potential contributions of protease activated receptors related mediators in allergic inflammation.Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:829068. doi: 10.1155/2014/829068. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Mediators Inflamm. 2014. PMID: 24876677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterizing Modulators of Protease-activated Receptors with a Calcium Mobilization Assay Using a Plate Reader.J Vis Exp. 2024 May 24;(207):10.3791/66507. doi: 10.3791/66507. J Vis Exp. 2024. PMID: 38856211 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of indole derived protease-activated receptor 4 antagonists and characterization in human platelets.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 11;8(6):e65528. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065528. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23776495 Free PMC article.
-
Protease-activated receptors (PARs): mechanisms of action and potential therapeutic modulators in PAR-driven inflammatory diseases.Thromb J. 2019 Mar 29;17:4. doi: 10.1186/s12959-019-0194-8. eCollection 2019. Thromb J. 2019. PMID: 30976204 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jackson T. Pharmacol Ther. 1991;50:425–442. - PubMed
-
- Trumpp-Kallmeyer S, Hoflack J, Bruinvels A, Hibert M. J Med Chem. 1992;35:3448–3462. - PubMed
-
- Strader C D, Fong T M, Tota M R, Underwood D, Dixon R A F. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:101–132. - PubMed
-
- Strader C D, Fong T M, Graziano M P, Tota M R. FASEB J. 1995;9:745–754. - PubMed
-
- Gudermann T, Nürnberg B, Schultz G. J Mol Med. 1995;73:51–63. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

