Sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c is a major mediator of insulin action on the hepatic expression of glucokinase and lipogenesis-related genes
- PMID: 10535992
- PMCID: PMC23076
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.22.12737
Sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c is a major mediator of insulin action on the hepatic expression of glucokinase and lipogenesis-related genes
Abstract
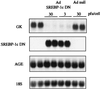
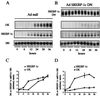
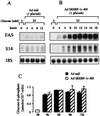
Hepatic glucokinase plays a key role in glucose metabolism as underlined by the anomalies associated with glucokinase mutations and the consequences of tissue-specific knock-out. In the liver, glucokinase transcription is absolutely dependent on the presence of insulin. The cis-elements and trans-acting factors that mediate the insulin effect are presently unknown; this is also the case for most insulin-responsive genes. We have shown previously that the hepatic expression of the transcription factor sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) is activated by insulin. We show here in primary cultures of hepatocytes that the adenovirus-mediated transduction of a dominant negative form of SREBP-1c inhibits the insulin effect on endogenous glucokinase expression. Conversely, in the absence of insulin, the adenovirus-mediated transduction of a dominant positive form of SREBP-1c overcomes the insulin dependency of glucokinase expression. Hepatic fatty acid synthase and Spot-14 are insulin/glucose-dependent genes. For this latter class of genes, the dominant positive form of SREBP-1c obviates the necessity for the presence of insulin, whereas glucose potentiates the effect of SREBP-1c on their expression. In addition, the insulin dependency of lipid accumulation in cultured hepatocytes is overcome by the dominant positive form of SREBP-1c. We propose that SREBP-1c is a major mediator of insulin action on hepatic gene expression and a key regulator of hepatic glucose/lipid metabolism.
Figures





Comment in
-
ADD-1 provides major new insight into the mechanism of insulin action.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Dec 7;96(25):14191-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.25.14191. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10588675 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

