Purification and characterization of (per)chlorate reductase from the chlorate-respiring strain GR-1
- PMID: 10542172
- PMCID: PMC94135
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.21.6706-6711.1999
Purification and characterization of (per)chlorate reductase from the chlorate-respiring strain GR-1
Abstract
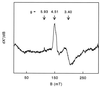
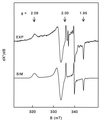
Strain GR-1 is one of several recently isolated bacterial species that are able to respire by using chlorate or perchlorate as the terminal electron acceptor. The organism performs a complete reduction of chlorate or perchlorate to chloride and oxygen, with the intermediate formation of chlorite. This study describes the purification and characterization of the key enzyme of the reductive pathway, the chlorate and perchlorate reductase. A single enzyme was found to catalyze both the chlorate- and perchlorate-reducing activity. The oxygen-sensitive enzyme was located in the periplasm and had an apparent molecular mass of 420 kDa, with subunits of 95 and 40 kDa in an alpha(3)beta(3) composition. Metal analysis showed the presence of 11 mol of iron, 1 mol of molybdenum, and 1 mol of selenium per mol of heterodimer. In accordance, quantitative electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy showed the presence of one [3Fe-4S] cluster and two [4Fe-4S] clusters. Furthermore, two different signals were ascribed to Mo(V). The K(m) values for perchlorate and chlorate were 27 and <5 microM, respectively. Besides perchlorate and chlorate, nitrate, iodate, and bromate were also reduced at considerable rates. The resemblance of the enzyme to nitrate reductases, formate dehydrogenases, and selenate reductase is discussed.
Figures


References
-
- Aasa R, Vänngård T. EPR signal intensity and powder shapes: a reexamination. J Magn Reson. 1975;19:308–315.
-
- Attaway H, Smith M. Reduction of perchlorate by an anaerobic enrichment culture. J Ind Microbiol. 1993;12:408–412.
-
- Bell L C, Richardson D J, Ferguson S J. Periplasmic and membrane-bound respiratory nitrate reductases in Thiosphaera pantotropha; the periplasmic enzyme catalyzes the first step in aerobic denitrification. FEBS Lett. 1993;265:85–87. - PubMed
-
- Bergmeyer H U. Methods of enzymatic analysis. New York, N.Y: Academic Press; 1963.
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

