Erythromycin inhibits transcriptional activation of NF-kappaB, but not NFAT, through calcineurin-independent signaling in T cells
- PMID: 10543746
- PMCID: PMC89542
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.43.11.2678
Erythromycin inhibits transcriptional activation of NF-kappaB, but not NFAT, through calcineurin-independent signaling in T cells
Abstract
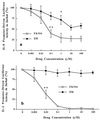
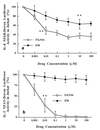
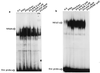
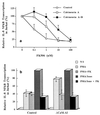
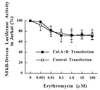
The molecular mechanism of the anti-inflammatory effect of erythromycin (EM) was investigated at the level of transcriptional regulation of cytokine gene expression in T cells. EM (>10(-6) M) significantly inhibited interleukin-8 (IL-8) expression but not IL-2 expression from T cells induced with 20 ng of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) per ml plus 2 microM calcium ionophore (P-I). In electrophoretic mobility shift assays EM at 10(-7) to 10(-5) M concentrations inhibited nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) DNA-binding activities induced by P-I. Reporter gene assays also showed that EM (10(-5) M) inhibited IL-8 NF-kappaB transcription by 37%. The inhibitory effects of EM on transcriptional activation of IL-2 and DNA-binding activity of nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) were not seen in T cells. On the other hand, FK506, which is also a macrolide derivative, inhibited transcriptional activation of both NF-kappaB and NFAT more strongly than EM did. The mechanism of EM inhibition of transactivation of NF-kappaB was further investigated in transiently transfected T cells that express calcineurin A and B subunits. Expression of calcineurin did not render transactivation of NF-kappaB in T cells more resistant to EM, while the inhibitory effect of FK506 on transactivation of NF-kappaB was attenuated. These findings indicate that EM is capable of inhibiting expression of the IL-8 gene in T cells through transcriptional inhibition and that this inhibition is mediated through a non-calcineurin-dependent signaling event in T lymphocytes.
Figures
References
-
- Aoki Y, Qiu D, Uyei A, Kao P N. Human airway epithelial cells express interleukin-2 in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1997;272:L276–L286. - PubMed
-
- Aoki Y, Kao P N. CyclosporinA-sensitive calcium signaling represses NFκB activation in human bronchial epithelial cells and enhances NFκB activation in Jurkat T-cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;234:424–431. - PubMed
-
- Aoki Y, Qiu D, Zhao G, Kao P N. Leukotriene B mediates histamine induction of NF-κB and IL-8 in human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1998;274:L1030–L1039. - PubMed
-
- Aoki Y, Zhao G, Qiu D, Shi L, Kao P N. CsA-sensitive purine-box transcriptional regulator in bronchial epithelial cells contains NF45, NF90, and Ku. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:L1164–L1172. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle P A, Henkel T. Function and activation of NFκB in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

