In vitro susceptibilities of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to fatty acids and monoglycerides
- PMID: 10543766
- PMCID: PMC89562
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.43.11.2790
In vitro susceptibilities of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to fatty acids and monoglycerides
Abstract
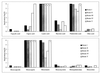
The susceptibility of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to several medium-chain fatty acids and their 1-monoglycerides was tested at a short inactivation time of 1 min. The results indicate that monocaprin, a monoglyceride of capric acid (10 carbon atoms, no double bonds), causes the fastest and most effective killing of all strains of N. gonorrhoeae tested.
Figures
References
-
- Australian Gonococcal Surveillance Programme. Annual report 1997. Commun Dis Intell. 1998;22:212–216. - PubMed
-
- Bergsson G, Steingrímsson Ó, Thormar H. Microbicidal effect of lipids against gram-positive and gram-negative cocci. Icelandic Med J. 1998;84(Suppl. 37):118.
-
- Bjekic M, Vlajinac H, Sipetic S. Incidence of gonorrhea in Belgrade, 1988–1994. J Infect. 1998;37:44–47. - PubMed
-
- Elias C J, Heise L L. Challenges for the development of female-controlled vaginal microbicides. AIDS. 1994;8:1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

