Characterization of an operon encoding two c-type cytochromes, an aa(3)-type cytochrome oxidase, and rusticyanin in Thiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC 33020
- PMID: 10543786
- PMCID: PMC91644
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.11.4781-4787.1999
Characterization of an operon encoding two c-type cytochromes, an aa(3)-type cytochrome oxidase, and rusticyanin in Thiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC 33020
Abstract
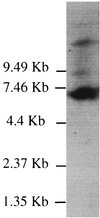
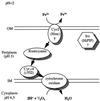
Despite the importance of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans in bioremediation and bioleaching, little is known about the genes encoding electron transfer proteins implicated in its energetic metabolism. This paper reports the sequences of the four cox genes encoding the subunits of an aa(3)-type cytochrome c oxidase. These genes are in a locus containing four other genes: cyc2, which encodes a high-molecular-weight cytochrome c; cyc1, which encodes a c(4)-type cytochrome (c(552)); open reading frame 1, which encodes a putative periplasmic protein of unknown function; and rus, which encodes rusticyanin. The results of Northern and reverse transcription-PCR analyses indicated that these eight genes are cotranscribed. Two transcriptional start sites were identified for this operon. Upstream from each of the start sites was a sigma70-type promoter recognized in Escherichia coli. While transcription in sulfur-grown T. ferrooxidans cells was detected from the two promoters, transcription in ferrous-iron-grown T. ferrooxidans cells was detected only from the downstream promoter. The cotranscription of seven genes encoding redox proteins suggests that all these proteins are involved in the same electron transfer chain; a model taking into account the biochemistry and the genetic data is discussed.
Figures


References
-
- Altschul S F, Gish W. Local alignment statistics. Methods Enzymol. 1996;266:460–480. - PubMed
-
- Appia-Ayme C, Bengrine A, Cavazza C, Giudici-Orticoni M-T, Bruschi M, Chippaux M, Bonnefoy V. Characterization and expression of the cotranscribed cyc1 and cyc2 genes encoding the cytochrome c4 (c552) and a high molecular weight cytochrome c from Thiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC33020. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1998;167:171–177. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: Greene Publishing; 1992.
-
- Bengrine A, Guiliani N, Appia-Ayme C, Jedlicki E, Holmes D S, Chippaux M, Bonnefoy V. Sequence and expression of the rusticyanin structural gene from Thiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC33020 strain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1443:99–112. - PubMed
-
- Blake R C, II, Shute E A. Respiratory enzymes of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Kinetic properties of an acid-stable iron:rusticyanin oxidoreductase. Biochemistry. 1994;33:9220–9228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

