Effect of various ions, pH, and osmotic pressure on oxidation of elemental sulfur by Thiobacillus thiooxidans
- PMID: 10543839
- PMCID: PMC91697
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.11.5163-5168.1999
Effect of various ions, pH, and osmotic pressure on oxidation of elemental sulfur by Thiobacillus thiooxidans
Abstract
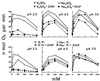
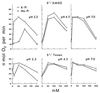
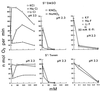
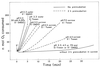
The oxidation of elemental sulfur by Thiobacillus thiooxidans was studied at pH 2.3, 4.5, and 7.0 in the presence of different concentrations of various anions (sulfate, phosphate, chloride, nitrate, and fluoride) and cations (potassium, sodium, lithium, rubidium, and cesium). The results agree with the expected response of this acidophilic bacterium to charge neutralization of colloids by ions, pH-dependent membrane permeability of ions, and osmotic pressure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduction of Mo6+ with elemental sulfur by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans.J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5956-9. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5956-5959.1988. J Bacteriol. 1988. PMID: 3056928 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of clays on the behavior of acidophilic Thiobacillus strains in suspensions].Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1979;19(9):643-51. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630190906. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1979. PMID: 397686 German. No abstract available.
-
Rate of elemental sulfur oxidation in some soils of Egypt as affected by the salinity level, moisture, texture, temperature and inoculation.Beitr Trop Landwirtsch Veterinarmed. 1976;14(2):179-85. Beitr Trop Landwirtsch Veterinarmed. 1976. PMID: 11771
-
Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans and its potential application.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Oct;103(19):7819-7833. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-10098-5. Epub 2019 Aug 28. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31463545 Review.
-
The acidophilic thiobacilli and other acidophilic bacteria that share their habitat.Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:265-92. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.001405. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984. PMID: 6388492 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Osmotic Imbalance, Cytoplasm Acidification and Oxidative Stress Induction Support the High Toxicity of Chloride in Acidophilic Bacteria.Front Microbiol. 2019 Oct 29;10:2455. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02455. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31736901 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic membrane fluidity and fatty acid composition of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans in response to pH stress.Extremophiles. 2010 Sep;14(5):427-41. doi: 10.1007/s00792-010-0319-2. Epub 2010 Jun 27. Extremophiles. 2010. PMID: 20582711
-
Uncovering the Mechanisms of Halotolerance in the Extremely Acidophilic Members of the Acidihalobacter Genus Through Comparative Genome Analysis.Front Microbiol. 2019 Feb 8;10:155. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00155. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30853944 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the fluoride-resistant regulation mechanism of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC 23270 based on whole genome microarrays.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 Oct;43(10):1441-53. doi: 10.1007/s10295-016-1827-6. Epub 2016 Aug 12. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27519020
-
Reduction of arsenic content in a complex galena concentrate by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans.BMC Biotechnol. 2004 Oct 13;4:22. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-4-22. BMC Biotechnol. 2004. PMID: 15482595 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander B, Leach S, Ingledew W J. The relationship between chemiosmotic parameters and sensitivity to anions and organic acids in the acidophile Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Gen Microbiol. 1987;133:1171–1179.
-
- Cobley J G. The maintenance of pH gradients in acidophilic and alkalophilic bacteria: Gibbs-Donnan equilibrium calculations. In: Strohl W R, Tuovinen O H, editors. Microbial chemoautotrophy. Columbus, Ohio: The Ohio State University Press; 1984. pp. 121–132.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

