Effect of various ions, pH, and osmotic pressure on oxidation of elemental sulfur by Thiobacillus thiooxidans
- PMID: 10543839
- PMCID: PMC91697
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.11.5163-5168.1999
Effect of various ions, pH, and osmotic pressure on oxidation of elemental sulfur by Thiobacillus thiooxidans
Abstract
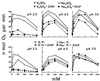
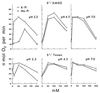
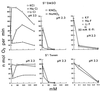
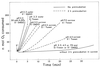
The oxidation of elemental sulfur by Thiobacillus thiooxidans was studied at pH 2.3, 4.5, and 7.0 in the presence of different concentrations of various anions (sulfate, phosphate, chloride, nitrate, and fluoride) and cations (potassium, sodium, lithium, rubidium, and cesium). The results agree with the expected response of this acidophilic bacterium to charge neutralization of colloids by ions, pH-dependent membrane permeability of ions, and osmotic pressure.
Figures
References
-
- Alexander B, Leach S, Ingledew W J. The relationship between chemiosmotic parameters and sensitivity to anions and organic acids in the acidophile Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Gen Microbiol. 1987;133:1171–1179.
-
- Cobley J G. The maintenance of pH gradients in acidophilic and alkalophilic bacteria: Gibbs-Donnan equilibrium calculations. In: Strohl W R, Tuovinen O H, editors. Microbial chemoautotrophy. Columbus, Ohio: The Ohio State University Press; 1984. pp. 121–132.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

