Comparison of the effects of divalent cations on the noradrenaline-evoked cation current in rabbit portal vein smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 10545143
- PMCID: PMC2269615
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.00771.x
Comparison of the effects of divalent cations on the noradrenaline-evoked cation current in rabbit portal vein smooth muscle cells
Abstract
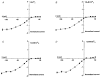
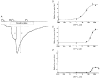
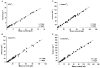
1. The facilitatory effects of external Ca2+, Sr2+ and Ba2+ (Ca2+o, Sr2+o and Ba2+o) on the noradrenaline-evoked non-selective cation current (Icat) were compared in rabbit portal vein smooth muscle cells using patch pipette techniques. 2. All divalent cations tested potentiated the amplitude of Icat and the potency sequence was Ca2+o > Sr2+o > Ba2+o. Ca2+o and Sr2+o increased the amplitude of Icat by about eight times whereas Ba2+o produced only a threefold facilitation. 3. The current-voltage relationship of Icat was not changed by Ca2+o, Sr2+o or Ba2+o. 4. From noise analysis the single channel conductance (gamma) was approximately 10 pS in divalent cation-free solution but was about 20 pS with Ca2+o, Sr2+o and Ba2+o. 5. From noise and voltage-jump experiments it was apparent that at least three kinetically resolvable channel states are associated with Icat in divalent cation-free solution. Ca2+o and Sr2+o produced marked changes in the characteristics of the power spectrum and relaxations of Icat in response to voltage steps, consistent with a shift in the equilibrium between the channel states, whereas Ba2+o produced minimal effects. 6. The data show that Ca2+o, Sr2+o and Ba2+o increase the amplitude of Icat, which results in part from an increase in the single channel conductance. In addition the results suggest that Ca2+o and Sr2+o alter the kinetic behaviour of the single channels whereas Ba2+o has little effect on the equilibrium between the channel states.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

