Activation of caspase-3 in single neurons and autophagic granules of granulovacuolar degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Evidence for apoptotic cell death
- PMID: 10550301
- PMCID: PMC1866960
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65460-0
Activation of caspase-3 in single neurons and autophagic granules of granulovacuolar degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Evidence for apoptotic cell death
Abstract
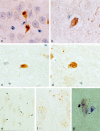
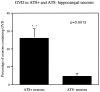
Neuronal loss is prominent in Alzheimer's disease (AD), and its mechanisms remain unresolved. Apoptotic cell death has been implicated on the basis of studies demonstrating DNA fragmentation and an up-regulation of proapoptotic proteins in the AD brain. However, DNA fragmentation in neurons is too frequent to account for the continuous neuronal loss in a degenerative disease extending over many years. Furthermore, the typical apoptotic morphology has not been convincingly documented in AD neurons with fragmented DNA. We report the detection of the activated form of caspase-3, the central effector enzyme of the apoptotic cascade, in AD and Down's syndrome (DS) brain using an affinity-purified antiserum. In AD and DS, single neurons with apoptotic morphology showed cytoplasmic immunoreactivity for activated caspase-3, whereas no neurons were labeled in age-matched controls. Apoptotic neurons were identified at an approximate frequency of 1 in 1100 to 5000 neurons in the cases examined. Furthermore, caspase-3 immunoreactivity was detected in granules of granulovacuolar degeneration. Our results provide direct evidence for apoptotic neuronal death in AD with a frequency compatible with the progression of neuronal degeneration in this chronic disease and identify autophagic vacuoles of granulovacuolar degeneration as possible means for the protective segregation of early apoptotic alterations in the neuronal cytoplasm.
Figures
References
-
- Yamatsuji T, Matsui T, Okamoto T, Komatsuzaki K, Takeda S, Fukumoto H, Iwatsubo T, Suzuki N, Asami-Odaka A, Ireland S, Kinane B, Giambarella U, Nishimoto I: G-protein-mediated neuronal DNA fragmentation induced by familial Alzheimer’s disease-associated mutants of APP. Science 1996, 272:1349-1352 - PubMed
-
- Vito P, Lacaná E, D’Adamio L: Interfering with apoptosis: Ca2+-binding protein ALG-2 and Alzheimer’s disease gene ALG-3. Science 1996, 271:521-524 - PubMed
-
- Wolozin B, Iwasaki K, Vito P, Ganjei JK, Lacaná E, Sunderland T, Zhao B, Kusiak JW, Wasco W, D’Adamio L: Participation of presenilin 2 in apoptosis: enhanced basal activity conferred by an Alzheimer mutation. Science 1996, 274:1710-1713 - PubMed
-
- Gschwind M, Huber G: Apoptotic cell death induced by β-amyloid 1–42 peptide is cell type dependent. J Neurochem 1995, 65:292-300 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

