Motility induced by human immunodeficiency virus-1 Tat on Kaposi's sarcoma cells requires platelet-activating factor synthesis
- PMID: 10550329
- PMCID: PMC1866979
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65488-0
Motility induced by human immunodeficiency virus-1 Tat on Kaposi's sarcoma cells requires platelet-activating factor synthesis
Abstract
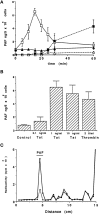
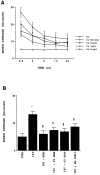
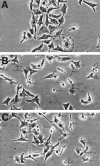
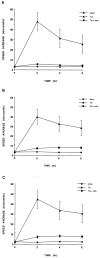
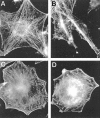
In the present study, we evaluated whether motility of Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) spindle cells induced by HIV-1 Tat protein is dependent on the synthesis of platelet-activating factor (PAF). The results obtained indicate that Tat induced a dose-dependent synthesis of PAF from KS cells at a concentration as low as 0.1 ng/ml. PAF production started rapidly after Tat stimulation, peaking at 30 minutes and declining thereafter. Tat-induced cell migration was also a rapid event starting at 30 minutes. The motility was abrogated by addition of a panel of chemically unrelated PAF receptor antagonists (WEB 2170, CV 3988, CV 6209, and BN 52021), suggesting that the synthesized PAF mediates the motogenic effect of Tat. This effect was also present on cells plated on a type-I collagen-, fibronectin-, or basement membrane extract-coated surface. Expression of PAF receptor-specific mRNA was detected in KS cells. In addition, examination of the cytoskeletal organization showed that Tat-mediated KS cell redistribution of actin filaments and shape change was also inhibited by a PAF receptor antagonist. Moreover, PAF receptor blockade prevented the up-regulation of beta1 integrin and the down-regulation of alphavbeta3 observed after stimulation of KS cells with Tat. In conclusion, the results of the present study indicate that Tat-induced PAF synthesis plays a critical role in triggering the events involved in motility of KS cells.
Figures



References
-
- Ensoli B, Barillari G, Gallo RC: Cytokine and growth factors in the pathogenesis of AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma. Immunol Rev 1992, 127:147-155 - PubMed
-
- Masood R, Cai J, Law R, Gill P: AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma pathogenesis, clinical features, and treatment. J Opin Oncol 1993, 5:831-834 - PubMed
-
- Rabkin CS, Janz S, Lash A, Coleman AE, Musaba E, Liotta L, Biggar R, Zhuang Z: Monoclonal origin of multicentric Kaposi’s sarcoma lesions. N Engl J Med 1997, 336:988-993 - PubMed
-
- Ensoli B, Barillari G, Buonaguro L, Gallo RC: Molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma. Adv Exp Med Biol 1991, 303:27-38 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

