An adenosine A3 receptor-selective agonist does not modulate calcium-activated potassium currents in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons
- PMID: 10551004
- PMCID: PMC3449169
- DOI: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)63562-1
An adenosine A3 receptor-selective agonist does not modulate calcium-activated potassium currents in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons
Figures
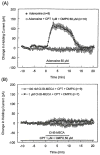
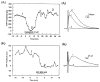



References
-
- Abbracchio MP, Brambilla R, Ceruti S, Kim HO, von Lubitz DKJE, Jacobson KA, Cattabeni F. G protein-dependent activation of phospholipase C by adenosine A3 receptors in rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1995;48:1038–1045. - PubMed
-
- Abdul-Ghani MA, Valiante TA, Carlen PL, Penne-father PS. Metabotropic glutamate receptors coupled to IP3 production mediate inhibition of IAHP in rat dentate granule neurons. J Neurophys. 1996;76:2691–2700. - PubMed
-
- Ali H, Cunha-Melo JR, Saul WF, Beaven MA. Activation of phospholipase C via adenosine receptors provides synergistic signals for secretion in antigen-stimulated RBL-2H3 cells. Evidence for a novel adenosine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:745–753. - PubMed
-
- Auchampach JA, Rizvi A, Qiu Y, Tang XL, Maldonado C, Teschner S, Bolli R. Selective activation of A3 adenosine receptors with N6-(3- iodobenzyl)adenosine-5′-N-methyluronamide protects against myocardial stunning and infarction without hemodynamic changes in conscious rabbits. Circ Res. 1997;80:800–809. - PubMed
-
- Blanton MG, Lo Turco JJ, Kriegstein AR. Whole cell recording from neurons in slices of reptilian and mammalian cerebral cortex. J Neurosci Meth. 1989;30:203–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

