Adrenergic and purinergic components in bisected vas deferens from spontaneously hypertensive rats
- PMID: 10556921
- PMCID: PMC1571703
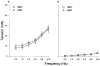
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702845
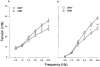
Adrenergic and purinergic components in bisected vas deferens from spontaneously hypertensive rats
Abstract
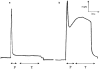
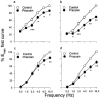
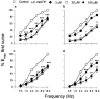
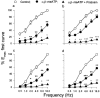
1. Purinergic and adrenergic components of the contractile response to electrical field stimulation (EFS) have been investigated in epididymal and prostatic portions of Wystar Kyoto (WKY) and spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR) vas deferens. 2. In both halves of SHR and WKY vas deferens, EFS (40 V, 0.5 ms for 30 s, 0.5-32 Hz) evoked frequency-related contractions. The neurogenic responses were biphasic, consisting of a rapid non-adrenergic response, dominant in the prostatic portion, followed by a slow tonic adrenergic component, dominant in the epididymal half. 3. Phasic and tonic components of the frequency-response curves evoked by EFS were significantly higher in the epididymal but not in the prostatic portion of vas deferens from SHR compared to WKY rats. 4. The alpha1-adrenoceptor antagonist prazosin (0.1 microM) was more effective against both components of the contractile response in the epididymal end of SHR than in WKY rats. 5. Inhibition by alpha, beta-methylene adenosine 5'-triphosphate (alpha,beta-meATP 3 and 30 microM) was higher in both components of the contractile responses in WKY preparations than in SHR. 6. Combined alpha1-adrenoceptor and P2x-purinoceptor antagonism virtually abolished the EFS-evoked contractile response in both strains. The degree of inhibition by prazosin (0.1 microM) after P2x-purinoceptor blockade was higher in SHR than in WKY rats. 7. These results demonstrate a modification in the purinergic and noradrenergic contribution to neurogenic responses in SHR and WKY animals besides a co-participation of ATP and noradrenaline in both contractile components of the response to EFS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hyperreactivity of alpha 1-adrenoceptors, but not of P2X-purinoceptors, in vas deferens of spontaneously hypertensive rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 9;199(3):303-7. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90493-a. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991. PMID: 1655481
-
Effects of hypophysectomy on purinergic and noradrenergic contractility of the rat vas deferens.J Auton Pharmacol. 1996 Aug;16(4):191-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1996.tb00422.x. J Auton Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8953373
-
Neocuproine, a copper (I) chelator, potentiates purinergic component of vas deferens contractions elicited by electrical field stimulation.Pharmacology. 2005 Oct;75(2):69-75. doi: 10.1159/000087007. Epub 2005 Jul 11. Pharmacology. 2005. PMID: 16020948
-
Autoinhibition, sympathetic cotransmission and biphasic contractile responses to trains of nerve stimulation in the rodent vas deferens.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1998 Dec;25(12):965-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1998.tb02169.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9887992 Review.
-
Fertility: purinergic receptors and the male contraceptive pill.Curr Biol. 2000 Apr 20;10(8):R305-7. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00436-x. Curr Biol. 2000. PMID: 10801405 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of nerve-evoked contractions of the murine vas deferens.Purinergic Signal. 2024 Oct;20(5):547-557. doi: 10.1007/s11302-024-09993-y. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Purinergic Signal. 2024. PMID: 38374492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BROCK J.A., CUNNANE T.C., STARKE K., WARDELL C.F. α2-Adrenoceptor autoinhibition of sympathetic transmitter release in guinea-pig vas deferens studied by intracellular and focal extracellular recording of junction potentials and currents. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 1990;342:45–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

