Protein kinase C co-expression and the effects of halothane on rat skeletal muscle sodium channels
- PMID: 10556936
- PMCID: PMC1571721
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702877
Protein kinase C co-expression and the effects of halothane on rat skeletal muscle sodium channels
Abstract
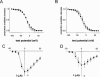
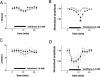
1. Voltage-gated Na channels, which are potential targets for general anaesthetics, are substrates for PKC, which phosphorylates a conserved site in the channel inactivation gate. We investigated the idea that PKC modulates the effect of volatile anaesthetics on Na channels via phosphorylation of this inactivation gate site. 2. Na currents through rat skeletal muscle Na channel alpha-subunits expressed in Xenopus oocytes were measured by two-microelectrode voltage clamp in the presence of the volatile anaesthetic agent halothane (2-bromo-2-chloro-1,1,1-trifluroethane). PKC activity was modulated by co-expression of a constitutively active PKC alpha-isozyme. 3. Halothane (0.4 mM) had no effect on Na currents. With co-expression of PKC, however, halothane dose-dependently enhanced the rate of Na current decay and caused a small, but statistically significant reduction in Na current amplitude. 4. The enhancement of Na current decay was absent in a Na channel mutant in which the inactivation gate phosphorylation site was disabled. Effects of halothane on amplitude were independent of this mutation. 5. Co-expression of a PKC alpha-isozyme permits an effect of halothane to hasten current decay and reduce current amplitude, at least in part through interaction with the inactivation gate phosphorylation site. We speculate that the interaction between halothane and Na channels is direct, and facilitated by PKC activity and by phosphorylation of a site in the channel inactivation gate.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Sodium channel isoform-specific effects of halothane: protein kinase C co-expression and slow inactivation gating.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Aug;130(8):1785-92. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703487. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10952666 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Nav1.7 and Nav1.8 peripheral nerve sodium channels by protein kinase A and protein kinase C.J Neurophysiol. 2004 Apr;91(4):1556-69. doi: 10.1152/jn.00676.2003. Epub 2003 Dec 3. J Neurophysiol. 2004. PMID: 14657190
-
Analysis of the effects of halothane on Gi-coupled muscarinic M2 receptor signaling in Xenopus oocytes using a chimeric G alpha protein.Pharmacology. 2004 Nov;72(3):205-12. doi: 10.1159/000080106. Pharmacology. 2004. PMID: 15452370
-
Molecular properties of brain sodium channels: an important target for anticonvulsant drugs.Adv Neurol. 1999;79:441-56. Adv Neurol. 1999. PMID: 10514834 Review.
-
Sodium channels and the synaptic mechanisms of inhaled anaesthetics.Br J Anaesth. 2009 Jul;103(1):61-9. doi: 10.1093/bja/aep144. Epub 2009 Jun 9. Br J Anaesth. 2009. PMID: 19508978 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative effects of halogenated inhaled anesthetics on voltage-gated Na+ channel function.Anesthesiology. 2009 Mar;110(3):582-90. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e318197941e. Anesthesiology. 2009. PMID: 19225394 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium channel isoform-specific effects of halothane: protein kinase C co-expression and slow inactivation gating.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Aug;130(8):1785-92. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703487. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10952666 Free PMC article.
-
PKC regulation of ion channels: The involvement of PIP2.J Biol Chem. 2022 Jun;298(6):102035. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102035. Epub 2022 May 16. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35588786 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- BABER J., ELLENA J.F., CAFISO D.S. Distribution of general anesthetics in phospholipid bilayers determined using 2H NMR and 1H-1H NOE spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1995;34:6533–6539. - PubMed
-
- BOURINET E., NARGEOT J., CHARNET P. Electrophysiological characterization of a TTX-sensitive sodium current in native Xenopus oocytes. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London-Series B: Biological Sciences. 1992;250:127–132. - PubMed
-
- BULJUBASIC N., RUSCH N.J., MARIJIC J., KAMPINE J.P., BOSNJAK Z.J. Effects of halothane and isoflurane on calcium and potassium channel currents in canine coronary arterial cells. Anesthesiology. 1992;76:990–998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

