Effects of luteolin and quercetin, inhibitors of tyrosine kinase, on cell growth and metastasis-associated properties in A431 cells overexpressing epidermal growth factor receptor
- PMID: 10556937
- PMCID: PMC1571723
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702879
Effects of luteolin and quercetin, inhibitors of tyrosine kinase, on cell growth and metastasis-associated properties in A431 cells overexpressing epidermal growth factor receptor
Abstract
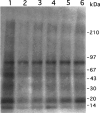
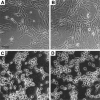
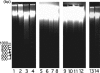
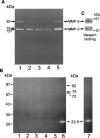
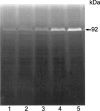
1. Flavonoids display a wide range of pharmacological properties including anti-inflammatory. Anti-mutagenic, anti-carcinogenic and anti-cancer effects. Here, we evaluated the effects of eight flavonoids on the tumour cell proliferation, cellular protein phosphorylation, and matrix metalloproteinase (MMPs) secretion. 2. Of the flavonoids examined, luteolin (Lu) and quercetin (Qu) were the two most potent agents, and significantly inhibited A431 cell proliferation with IC50 values of 19 and 21 micronM, respectively. 3. The epidermal growth factor (EGF) (10 nM) promoted growth of A431 cells (+25+/-4.6%) and mediated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase activity and autophosphorylation of EGFR were inhibited by Lu and Qu. At concentration of 20 micronM, both Lu and Qu markedly decreased the levels of phosphorylation of A431 cellular proteins, including EGFR. 4. A431 cells treated with Lu or Qu exhibited protuberant cytoplasmic blebs and progressive shrinkage morphology. Lu and Qu also time-dependently induced the appearance of a ladder pattern of DNA fragmentation, and this effect was abolished by EGF treatment. 5. The addition of EGF only marginally diminished the inhibitory effect of luteolin and quercetin on the growth rate of A431 cells, treatment of cellular proteins with EGF and luteolin or quercetin greatly reduced protein phosphorylation, indicating Lu and Qu may act effectively to inhibit a wide range of protein kinases, including EGFR tyrosine kinase. 6. EGF increased the levels of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), while Lu and Qu appeared to suppress the secretion of these two MMPs in A431 cells. 7. Examination of the relationship between the chemical structure and inhibitory effects of eight flavonoids reveal that the double bond between C2 and C3 in ring C and the OH groups on C3' and C4' in ring B are critical for the biological activities. 8. This study demonstrates that the inhibitory effects of Lu and Qu, and the stimulatory effects of EGF, on tumour cell proliferation, cellular protein phosphorylation, and MMP secretion may be mediated at least partly through EGFR. This study supports the idea that Lu and Qu may have potential as anti-cancer and anti-metastasis agents.
Figures
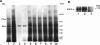
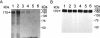
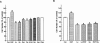

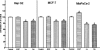
Similar articles
-
Blockade of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase activity by quercetin and luteolin leads to growth inhibition and apoptosis of pancreatic tumor cells.Anticancer Res. 2002 May-Jun;22(3):1615-27. Anticancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12168845
-
Transinactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and focal adhesion kinase phosphorylation by dietary flavonoids: effect on invasive potential of human carcinoma cells.Biochem Pharmacol. 2004 Jun 1;67(11):2103-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2004.02.023. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15135307
-
Effects of dietary flavonoids, luteolin, and quercetin on the reversal of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in A431 epidermal cancer cells.Cancer Sci. 2011 Oct;102(10):1829-39. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.02035.x. Epub 2011 Aug 10. Cancer Sci. 2011. PMID: 21752154
-
Design and synthesis of novel tyrosine kinase inhibitors using a pharmacophore model of the ATP-binding site of the EGF-R.J Pharm Belg. 1997 Mar-Apr;52(2):88-96. J Pharm Belg. 1997. PMID: 9193132 Review.
-
Specific inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase by 4-anilinoquinazolines.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1996;38(1):67-73. doi: 10.1007/BF01803785. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1996. PMID: 8825124 Review.
Cited by
-
Apolipoprotein E3 Containing Nanodiscs as Vehicles for Transport and Targeted Delivery of Flavonoid Luteolin.ACS Omega. 2024 Jan 3;9(2):2988-2999. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c09120. eCollection 2024 Jan 16. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38250386 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-carcinogenic effects of the flavonoid luteolin.Molecules. 2008 Oct 22;13(10):2628-2651. doi: 10.3390/molecules13102628. Molecules. 2008. PMID: 18946424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Plant-Derived Natural Products as a Regulator of the Tyrosine Kinase Pathway in the Management of Lung Cancer.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jun 30;47(7):498. doi: 10.3390/cimb47070498. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40728967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pomegranate and its components as alternative treatment for prostate cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Aug 25;15(9):14949-66. doi: 10.3390/ijms150914949. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25158234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective role of antioxidants capacity of Hyrtios aff. Erectus sponge extract against mixture of persistent organic pollutants (POPs)-induced hepatic toxicity in mice liver: biomarkers and ultrastructural study.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Sep;24(27):22061-22072. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9805-8. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28791578
References
-
- AGULLO G., GAMET-PAYRASTRE L., MANENTI S., VIALA C., REMESY C., CHAP H., PAYRASTRE B. Relationship between flavonoid structure and inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: a comparison with tyrosine kinase and protein kinase C. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1997;53:1649–1657. - PubMed
-
- AKIYAMA T., ISHIDA J., NAKAGAWA S., OGAWARA H., WATANABE S., ITOH N., SHIBUYA M., FUKAMI Y. Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1987;262:5592–5595. - PubMed
-
- ARMSTRONG D.K., ISACCS J.T., OTTAVINO Y.L., DARIDSON N.E. Programmed cell death in an estrogen-independent human cancer cell line, MDA-MB-468. Cancer Res. 1992;52:3418–3424. - PubMed
-
- BISHOP J.M. The molecular genetics of cancer. Science. 1987;235:305–311. - PubMed
-
- BRADFORD M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

