Protein kinase A antagonizes Hedgehog signaling by regulating both the activator and repressor forms of Cubitus interruptus
- PMID: 10557210
- PMCID: PMC317143
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.13.21.2828
Protein kinase A antagonizes Hedgehog signaling by regulating both the activator and repressor forms of Cubitus interruptus
Abstract
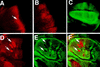
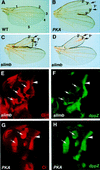
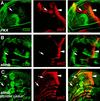
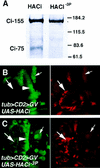
The Hedgehog (Hh) family of secreted proteins controls many aspects of animal development. In Drosophila, Hh transduces its signal via Cubitus interruptus (Ci), a transcription factor present in two forms: a full-length activator and a carboxy-terminally truncated repressor that is derived from the full-length form by proteolytic processing. The proteolytic processing of Ci is promoted by the activities of protein kinase A (PKA) and Slimb, whereas it is inhibited by Hh. Here we show that PKA inhibits the activity of the full-length Ci in addition to its role in regulating Ci proteolysis. Whereas Ci processing is blocked in both PKA and slimb mutant cells, the accumulated full-length Ci becomes activated only in PKA but not in slimb mutant cells. Moreover, PKA inhibits an uncleavable activator form of Ci. These observations suggest that PKA regulates the activity of the full-length Ci independent of its proteolytic processing. We also provide evidence that PKA regulates both the proteolytic processing and transcriptional activity of Ci by directly phosphorylating Ci. We propose that phosphorylation of Ci by PKA has two separable roles: (1) It blocks the transcription activity of the full-length activator form of Ci, and (2) it targets Ci for Slimb-mediated proteolytic processing to generate the truncated form that functions as a repressor.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Processing of the Drosophila hedgehog signaling effector Ci-155 to the repressor Ci-75 is mediated by direct binding to the SCF component Slimb.Curr Biol. 2006 Jan 10;16(1):110-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.12.012. Epub 2005 Dec 29. Curr Biol. 2006. PMID: 16386907
-
Phosphorylation by double-time/CKIepsilon and CKIalpha targets cubitus interruptus for Slimb/beta-TRCP-mediated proteolytic processing.Dev Cell. 2005 Dec;9(6):819-30. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.10.006. Dev Cell. 2005. PMID: 16326393
-
Protein kinase A directly regulates the activity and proteolysis of cubitus interruptus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Mar 3;95(5):2349-54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.5.2349. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9482888 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog signalling: Ci complex cuts and clasps.Curr Biol. 1997 Dec 1;7(12):R759-62. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(06)00398-8. Curr Biol. 1997. PMID: 9382827 Review.
-
Regulation of Hedgehog signaling: a complex story.Biochem Pharmacol. 2004 Mar 1;67(5):805-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2004.01.002. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15104233 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extensive crosstalk of G protein-coupled receptors with the Hedgehog signalling pathway.Development. 2021 Apr 1;148(7):dev189258. doi: 10.1242/dev.189258. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Development. 2021. PMID: 33653875 Free PMC article.
-
Multisite interaction with Sufu regulates Ci/Gli activity through distinct mechanisms in Hh signal transduction.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 May 19;112(20):6383-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1421628112. Epub 2015 May 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25941387 Free PMC article.
-
Smoothened regulates activator and repressor functions of Hedgehog signaling via two distinct mechanisms.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 17;281(11):7237-43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M510169200. Epub 2006 Jan 19. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16423832 Free PMC article.
-
The contributions of protein kinase A and smoothened phosphorylation to hedgehog signal transduction in Drosophila melanogaster.Genetics. 2006 Aug;173(4):2049-62. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.061036. Epub 2006 Jun 18. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16783001 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct protein degradation mechanisms mediated by Cul1 and Cul3 controlling Ci stability in Drosophila eye development.Genes Dev. 2002 Sep 15;16(18):2403-14. doi: 10.1101/gad.1011402. Genes Dev. 2002. PMID: 12231629 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alcedo J, Noll M. Hedgehog and its Patched-Smoothened receptor complex: a Novel signalling mechanism at the cell surface. Biol Cenm. 1997;378:583–590. - PubMed
-
- Alcedo J, Ayzenzon M, Von Ohlen T, Noll M, Hooper JE. The Drosophila smoothened gene encodes a seven-pass membrane protein, a putative receptor for the Hedgehog signal. Cell. 1996;86:231–232. - PubMed
-
- Alexandre C, Jacinto A, Ingham PW. Transcriptional activation of Hedgehog target genes in Drosophila is mediated directly by the Cubitus interruptus protein, a member of the GLI family of the zinc finger DNA-binding proteins. Genes & Dev. 1996;10:2003–2013. - PubMed
-
- Alves G, Limbourg-Bouchon B, Tricoire H, Brissard-Zahraoui J, Lamour-Isnard C, Busson D. Modulation of Hedgehog target gene expression by the Fused serine-threonine kinase in wing imaginal discs. Mech Dev. 1998;78:17–31. - PubMed
-
- Aza-Blanc P, Ramirez-Weber F, Laget M, Schwartz C, Kornberg T. Proteolysis that is inhibited by Hedgehog targets Cubitus interruptus protein to the nucleus and converts it to a repressor. Cell. 1997;89:1043–1053. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
