Crystal structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of hepatitis C virus
- PMID: 10557268
- PMCID: PMC23895
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.23.13034
Crystal structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of hepatitis C virus
Abstract
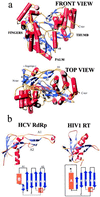
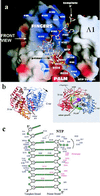
We report the crystal structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of hepatitis C virus, a major human pathogen, to 2.8-A resolution. This enzyme is a key target for developing specific antiviral therapy. The structure of the catalytic domain contains 531 residues folded in the characteristic fingers, palm, and thumb subdomains. The fingers subdomain contains a region, the "fingertips," that shares the same fold with reverse transcriptases. Superposition to the available structures of the latter shows that residues from the palm and fingertips are structurally equivalent. In addition, it shows that the hepatitis C virus polymerase was crystallized in a closed fingers conformation, similar to HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in ternary complex with DNA and dTTP [Huang H., Chopra, R., Verdine, G. L. & Harrison, S. C. (1998) Science 282, 1669-1675]. This superposition reveals the majority of the amino acid residues of the hepatitis C virus enzyme that are likely to be implicated in binding to the replicating RNA molecule and to the incoming NTP. It also suggests a rearrangement of the thumb domain as well as a possible concerted movement of thumb and fingertips during translocation of the RNA template-primer in successive polymerization rounds.
Figures

References
-
- Rice C M. In: Virology. Fields B N, Knipe D M, Howley P M, Chanock R M, Melnick J L, Monath T P, Roizman B, Straus S E, editors. Vol. 1. Philadelphia: Lippincott; 1996. pp. 931–959.
-
- Ollis D L, Brick P, Hamlin R, Xuong N G, Steitz T A. Nature (London) 1985;313:762–766. - PubMed
-
- Brautigam C A, Steitz T A. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998;8:54–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

