Homeostatic expansion and phenotypic conversion of naïve T cells in response to self peptide/MHC ligands
- PMID: 10557316
- PMCID: PMC23943
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.23.13306
Homeostatic expansion and phenotypic conversion of naïve T cells in response to self peptide/MHC ligands
Abstract
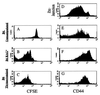
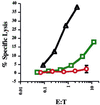
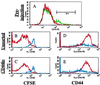
Recent data suggest that survival of resting, naïve T cells requires an interaction with self MHC molecules. From analysis of the class I MHC-restricted T cell receptor transgenic strain OT-I, we report a different response. Rather than merely surviving, these T cells proliferated slowly after transfer into T-depleted syngeneic hosts. This expansion required both T cell "space" and expression of normal levels of self class I MHC molecules. Furthermore, we demonstrate that during homeostatic expansion in a suitable environment, naïve phenotype (CD44(low)) OT-I T cells converted to memory phenotype (CD44(med/high)), despite the absence of foreign antigenic stimulation. On the other hand, cells undergoing homeostatic expansion did not acquire cytolytic effector function. The significance of these data for reactivity of T cells with self peptide/MHC ligands and the implications for normal and abnormal T cell homeostasis are discussed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Autologous regulation of naive T cell homeostasis within the T cell compartment.J Immunol. 2001 Feb 15;166(4):2460-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.4.2460. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11160306
-
Naive T cells transiently acquire a memory-like phenotype during homeostasis-driven proliferation.J Exp Med. 2000 Aug 21;192(4):557-64. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.4.557. J Exp Med. 2000. PMID: 10952725 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of avidity for major histocompatibility complex in homeostasis of naive and memory T cells.J Exp Med. 2003 Apr 21;197(8):1007-16. doi: 10.1084/jem.20021812. J Exp Med. 2003. PMID: 12707300 Free PMC article.
-
Homeostatic proliferation and survival of naïve and memory T cells.Eur J Immunol. 2009 Aug;39(8):2088-94. doi: 10.1002/eji.200939444. Eur J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19637200 Review.
-
Homeostasis of Naive and Memory T Lymphocytes.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2021 Sep 1;13(9):a037879. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a037879. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2021. PMID: 33753403 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunosenescence and organ transplantation.Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2013 Jul;27(3):65-75. doi: 10.1016/j.trre.2013.03.001. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2013. PMID: 23639337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age-related accumulation of T cells with markers of relatively stronger autoreactivity leads to functional erosion of T cells.BMC Immunol. 2012 Feb 9;13:8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-13-8. BMC Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22321827 Free PMC article.
-
A causal link between lymphopenia and autoimmunity.Immunol Lett. 2005 Apr 15;98(1):23-31. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2004.10.022. Epub 2004 Nov 24. Immunol Lett. 2005. PMID: 15790505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the role of MHC class II molecules in the survival and lymphopenia-induced proliferation of peripheral CD4+ T cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 May 13;100(10):6021-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1037754100. Epub 2003 Apr 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12719530 Free PMC article.
-
IL-7 enhances peripheral T cell reconstitution after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.J Clin Invest. 2003 Oct;112(7):1095-107. doi: 10.1172/JCI17865. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 14523046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fink P J, Bevan M J. Adv Immunol. 1995;59:99–133. - PubMed
-
- Freitas A A, Rocha B. Science. 1997;277:1950. - PubMed
-
- Benoist C, Mathis D. Science. 1997;276:2000–2001. - PubMed
-
- Marrack P, Mitchell T, Bender J, Hildeman D, Kedl R, Teague K, Kappler J. Immunol Rev. 1998;165:279–285. - PubMed
-
- Tanchot C, Lemmonnier F A, Perarnau B, Freitas A A, Rocha B. Science. 1997;276:2057–2062. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

