Homeostatic expansion and phenotypic conversion of naïve T cells in response to self peptide/MHC ligands
- PMID: 10557316
- PMCID: PMC23943
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.23.13306
Homeostatic expansion and phenotypic conversion of naïve T cells in response to self peptide/MHC ligands
Abstract
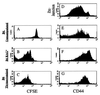
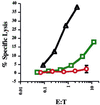
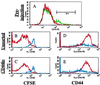
Recent data suggest that survival of resting, naïve T cells requires an interaction with self MHC molecules. From analysis of the class I MHC-restricted T cell receptor transgenic strain OT-I, we report a different response. Rather than merely surviving, these T cells proliferated slowly after transfer into T-depleted syngeneic hosts. This expansion required both T cell "space" and expression of normal levels of self class I MHC molecules. Furthermore, we demonstrate that during homeostatic expansion in a suitable environment, naïve phenotype (CD44(low)) OT-I T cells converted to memory phenotype (CD44(med/high)), despite the absence of foreign antigenic stimulation. On the other hand, cells undergoing homeostatic expansion did not acquire cytolytic effector function. The significance of these data for reactivity of T cells with self peptide/MHC ligands and the implications for normal and abnormal T cell homeostasis are discussed.
Figures


References
-
- Fink P J, Bevan M J. Adv Immunol. 1995;59:99–133. - PubMed
-
- Freitas A A, Rocha B. Science. 1997;277:1950. - PubMed
-
- Benoist C, Mathis D. Science. 1997;276:2000–2001. - PubMed
-
- Marrack P, Mitchell T, Bender J, Hildeman D, Kedl R, Teague K, Kappler J. Immunol Rev. 1998;165:279–285. - PubMed
-
- Tanchot C, Lemmonnier F A, Perarnau B, Freitas A A, Rocha B. Science. 1997;276:2057–2062. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

