Serine racemase: a glial enzyme synthesizing D-serine to regulate glutamate-N-methyl-D-aspartate neurotransmission
- PMID: 10557334
- PMCID: PMC23961
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.23.13409
Serine racemase: a glial enzyme synthesizing D-serine to regulate glutamate-N-methyl-D-aspartate neurotransmission
Abstract
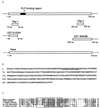
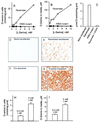
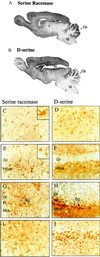
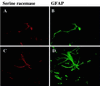
Although D amino acids are prominent in bacteria, they generally are thought not to occur in mammals. Recently, high levels of D-serine have been found in mammalian brain where it activates glutamate/N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors by interacting with the "glycine site" of the receptor. Because amino acid racemases are thought to be restricted to bacteria and insects, the origin of D-serine in mammals has been puzzling. We now report cloning and expression of serine racemase, an enzyme catalyzing the formation of D-serine from L-serine. Serine racemase is a protein representing an additional family of pyridoxal-5' phosphate-dependent enzymes in eukaryotes. The enzyme is enriched in rat brain where it occurs in glial cells that possess high levels of D-serine in vivo. Occurrence of serine racemase in the brain demonstrates the conservation of D-amino acid metabolism in mammals with implications for the regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate neurotransmission through glia-neuronal interactions.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

