A novel lipolytic enzyme located in the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 10559163
- PMCID: PMC94172
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.22.6977-6986.1999
A novel lipolytic enzyme located in the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
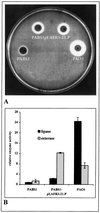
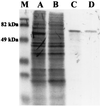
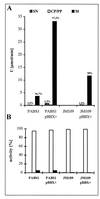
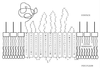
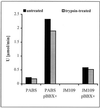
A lipase-negative deletion mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 still showed extracellular lipolytic activity toward short-chain p-nitrophenylesters. By screening a genomic DNA library of P. aeruginosa PAO1, an esterase gene, estA, was identified, cloned, and sequenced, revealing an open reading frame of 1,941 bp. The product of estA is a 69.5-kDa protein, which is probably processed by removal of an N-terminal signal peptide to yield a 67-kDa mature protein. A molecular mass of 66 kDa was determined for (35)S-labeled EstA by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and autoradiography. The amino acid sequence of EstA indicated that the esterase is a member of a novel GDSL family of lipolytic enzymes. The estA gene showed high similarity to an open reading frame of unknown function located in the trpE-trpG region of P. putida and to a gene encoding an outer membrane esterase of Salmonella typhimurium. Amino acid sequence alignments led us to predict that this esterase is an autotransporter protein which possesses a carboxy-terminal beta-barrel domain, allowing the secretion of the amino-terminal passenger domain harboring the catalytic activity. Expression of estA in P. aeruginosa and Escherichia coli and subsequent cell fractionation revealed that the enzyme was associated with the cellular membranes. Trypsin treatment of whole cells released a significant amount of esterase, indicating that the enzyme was located in the outer membrane with the catalytic domain exposed to the surface. To our knowledge, this esterase is unique in that it exemplifies in P. aeruginosa (i) the first enzyme identified in the outer membrane and (ii) the first example of a type IV secretion mechanism.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Use of Pseudomonas putida EstA as an anchoring motif for display of a periplasmic enzyme on the surface of Escherichia coli.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004 Dec;70(12):6968-76. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.12.6968-6976.2004. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15574889 Free PMC article.
-
The autotransporter esterase EstA of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is required for rhamnolipid production, cell motility, and biofilm formation.J Bacteriol. 2007 Sep;189(18):6695-703. doi: 10.1128/JB.00023-07. Epub 2007 Jul 13. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17631636 Free PMC article.
-
A generic system for the Escherichia coli cell-surface display of lipolytic enzymes.FEBS Lett. 2005 Feb 14;579(5):1177-82. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.12.087. FEBS Lett. 2005. PMID: 15710409
-
Cloning, expression and characterization of a novel cold‑adapted GDSL family esterase from Photobacterium sp. strain J15.Extremophiles. 2016 Jan;20(1):44-55. doi: 10.1007/s00792-015-0796-4. Extremophiles. 2016. PMID: 26475626
-
Autotransporters with GDSL passenger domains: molecular physiology and biotechnological applications.Chembiochem. 2011 Jul 4;12(10):1476-85. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201100013. Epub 2011 May 19. Chembiochem. 2011. PMID: 21598370 Review.
Cited by
-
Specific association of lectin LecB with the surface of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: role of outer membrane protein OprF.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46857. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046857. Epub 2012 Oct 8. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23056489 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Secretion Systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An Essay on Diversity, Evolution, and Function.Front Microbiol. 2011 Jul 18;2:155. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2011.00155. eCollection 2011. Front Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21811488 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional characterisation of TesA - a novel lysophospholipase A from Pseudomonas aeruginosa.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 18;8(7):e69125. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069125. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23874889 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Moraxella catarrhalis outer membrane protein exhibiting both adhesin and lipolytic activities.Infect Immun. 2003 Aug;71(8):4341-50. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.8.4341-4350.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12874311 Free PMC article.
-
Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae p65 surface lipoprotein is a lipolytic enzyme with a preference for shorter-chain fatty acids.J Bacteriol. 2004 Sep;186(17):5790-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.17.5790-5798.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15317784 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akrim M, Bally M, Ball G, Tommassen J, Teerink H, Filloux A, Lazdunski A. Xcp-mediated protein secretion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: identification of two additional genes and evidence for regulation of xcp gene expression. Mol Microbiol. 1993;10:431–443. - PubMed
-
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Lipman D J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

