Isolation, cloning, and expression of an acid phosphatase containing phosphotyrosyl phosphatase activity from Prevotella intermedia
- PMID: 10559178
- PMCID: PMC94187
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.22.7107-7114.1999
Isolation, cloning, and expression of an acid phosphatase containing phosphotyrosyl phosphatase activity from Prevotella intermedia
Abstract
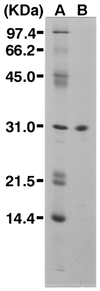
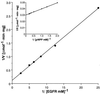
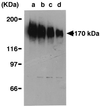
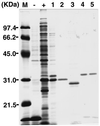
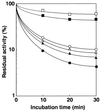
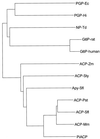
A novel acid phosphatase containing phosphotyrosyl phosphatase (PTPase) activity, designated PiACP, from Prevotella intermedia ATCC 25611, an anaerobe implicated in progressive periodontal disease, has been purified and characterized. PiACP, a monomer with an apparent molecular mass of 30 kDa, did not require divalent metal cations for activity and was sensitive to orthovanadate but highly resistant to okadaic acid. The enzyme exhibited substantial activity against tyrosine phosphate-containing peptides derived from the epidermal growth factor receptor. On the basis of N-terminal and internal amino acid sequences of purified PiACP, the gene coding for PiACP was isolated and sequenced. The PiACP gene consisted of 792 bp and coded for a basic protein with an M(r) of 29,164. The deduced amino acid sequence exhibited striking similarity (25 to 64%) to those of members of class A bacterial acid phosphatases, including PhoC of Morganella morganii, and involved a conserved phosphatase sequence motif that is shared among several lipid phosphatases and the mammalian glucose-6-phosphatases. The highly conservative motif HCXAGXXR in the active domain of PTPase was not found in PiACP. Mutagenesis of recombinant PiACP showed that His-170 and His-209 were essential for activity. Thus, the class A bacterial acid phosphatases including PiACP may function as atypical PTPases, the biological functions of which remain to be determined.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Purification and characterization of alkaline phosphatase containing phosphotyrosyl phosphatase activity from the bacterium Prevotella intermedia.FEBS Lett. 1998 May 29;428(3):157-60. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(98)00514-6. FEBS Lett. 1998. PMID: 9654126
-
Kinetic and site-directed mutagenesis studies of prevotella intermedia acid phosphatase.Protein Pept Lett. 2003 Feb;10(1):53-9. doi: 10.2174/0929866033408282. Protein Pept Lett. 2003. PMID: 12625826
-
Cloning of phosphatase I gene from a psychrophile, Shewanella sp., and some properties of the recombinant enzyme.J Biochem. 2000 Jan;127(1):143-9. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022576. J Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10731677
-
Structure and function of SH2-domain containing tyrosine phosphatases.Semin Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;4(6):419-32. doi: 10.1006/scel.1993.1050. Semin Cell Biol. 1993. PMID: 8305681 Review.
-
Bacterial nonspecific acid phosphohydrolases: physiology, evolution and use as tools in microbial biotechnology.Cell Mol Life Sci. 1998 Aug;54(8):833-50. doi: 10.1007/s000180050212. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1998. PMID: 9760992 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gene expression profile and pathogenicity of biofilm-forming Prevotella intermedia strain 17.BMC Microbiol. 2009 Jan 16;9:11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-11. BMC Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19146705 Free PMC article.
-
Use of the genomic subtractive hybridization technique to develop a real-time PCR assay for quantitative detection of Prevotella spp. in oral biofilm samples.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Jun;43(6):2948-51. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.6.2948-2951.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15956428 Free PMC article.
-
Polar localization of PhoN2, a periplasmic virulence-associated factor of Shigella flexneri, is required for proper IcsA exposition at the old bacterial pole.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 27;9(2):e90230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090230. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24587292 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of novel membrane-bound PRL protein tyrosine phosphatases from Setaria cervi, a bovine filarial parasite.Parasitol Res. 2015 Nov;114(11):4267-79. doi: 10.1007/s00436-015-4667-9. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Parasitol Res. 2015. PMID: 26341797
-
MALDI mass sequencing and biochemical characterization of Setaria cervi protein tyrosine phosphatase.Parasitol Res. 2013 Jan;112(1):147-54. doi: 10.1007/s00436-012-3118-0. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Parasitol Res. 2013. PMID: 23052758
References
-
- Ansai T, Yamashita Y, Awano S, Shibata Y, Wachi M, Nagai K, Takehara T. A murC gene in Porphyromonas gingivalis 381. Microbiology. 1995;141:2047–2052. - PubMed
-
- Ansai T, Dupuy L C, Barik S. Interactions between a minimal protein serine/threonine phosphatase and its phosphopeptide substrate sequence. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:24401–24407. - PubMed
-
- Ansai T, Awano S, Chen X C, Fuchi T, Arimoto T, Akifusa S, Takehara T. Purification and characterization of alkaline phosphatase containing phosphotyrosyl phosphatase activity from the bacterium Prevotella intermedia. FEBS Lett. 1998;428:157–160. - PubMed
-
- Ashimoto A, Chen C, Bakker I, Slots J. Polymerase chain reaction detection of 8 putative periodontal pathogens in subgingival plaque of gingivitis and advanced periodontitis lesions. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1996;11:266–273. - PubMed
-
- Barik S. Site-directed mutagenesis by PCR; substitution, insertion, deletion, and gene fusion. Methods Neurosci. 1995;26:309–323.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

