Transcriptional analysis of the rubrerythrin and superoxide dismutase genes of Clostridium perfringens
- PMID: 10559182
- PMCID: PMC94191
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.22.7136-7139.1999
Transcriptional analysis of the rubrerythrin and superoxide dismutase genes of Clostridium perfringens
Abstract
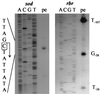
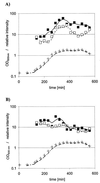
We cloned and sequenced a 2.7-kb fragment of chromosomal DNA from Clostridium perfringens containing the superoxide dismutase-encoding gene, sod. Previously, rubrerythrin from C. perfringens had been isolated and its gene (rbr) had been cloned (Y. Lehmann, L. Meile, and M. Teuber, J. Bacteriol. 178:7152-7158, 1996). Northern blot experiments revealed a length of approximately 800 bases for each transcript of rbr and sod of C. perfringens. Thus, rbr and sod each represent a monocistronic operon. Their transcription start points were located by primer extension analyses. sod transcription was shown to depend on the growth phase, and it reached a maximum during the transition from log phase to stationary phase. Neither sod nor rbr transcription was influenced by oxidative stress.
Figures



References
-
- Brehm K, Haas A, Goebel W, Kreft J. A gene encoding a superoxide dismutase of the facultative intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. Gene. 1992;118:121–125. - PubMed
-
- Coulter E D, Shenvi N V, Kurtz D M. NADH peroxidase activity of rubrerythrin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;255:317–323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

