Transcriptional up-regulation of the cyclin D2 gene and acquisition of new cyclin-dependent kinase partners in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-infected cells
- PMID: 10559304
- PMCID: PMC113041
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.12.9917-9927.1999
Transcriptional up-regulation of the cyclin D2 gene and acquisition of new cyclin-dependent kinase partners in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-infected cells
Abstract
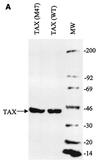
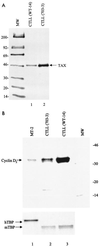
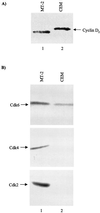
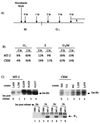
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) is the etiologic agent for adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL) and HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. Tax(1) is a 40-kDa phosphoprotein, predominantly localized in the nucleus of the host cell, which functions to transactivate both viral and cellular promoters. It seems likely that HTLV-1, through expression of the viral regulatory protein Tax(1), provides some initial alteration in cell metabolism predisposing the development of ATL. Here, we demonstrate that HTLV-1 infection in T-cell lines and patient samples causes overexpression of an early G(1) cyclin, cyclin D2. The transcriptional up-regulation of the cyclin D2 gene is due to activation of Tax on the cyclin D2 gene. More important, we find that overexpression of cyclin D2 is accompanied by acquisition of new partners such as cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (cdk2), cdk4, and cdk6 in infected cells. This is in contrast to uninfected T cells, where cyclin D2 associates only with cdk6. Functional effects of these cyclin-cdk complexes in infected cells are shown by hyperphosphorylation of Rb and histone H1, indicators of active progression into S phase as well as changes in cellular chromatin and transcription machinery. These studies link HTLV-1 infection with changes of cellular cyclin gene expression, hence providing clues to development of T-cell leukemia.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Overexpression of p21(waf1) in human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1-infected cells and its association with cyclin A/cdk2.J Virol. 2000 Aug;74(16):7270-83. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.16.7270-7283.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10906181 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of cell cycle progression induced by the oncogene product Tax of human T-cell leukemia virus type I.Oncogene. 2001 Apr 19;20(17):2055-67. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204304. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11360190
-
Physical interaction of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax with cyclin-dependent kinase 4 stimulates the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma protein.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 May;22(10):3327-38. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.10.3327-3338.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11971966 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin D2 activates Cdk2 in preference to Cdk4 in human breast epithelial cells.Oncogene. 1997 Mar 20;14(11):1329-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1200951. Oncogene. 1997. PMID: 9178893
-
Ras regulation of cyclin-dependent immunoprecipitation kinase assays.Methods Enzymol. 2001;333:127-38. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(01)33051-3. Methods Enzymol. 2001. PMID: 11400330 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Acetylated Tat regulates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 splicing through its interaction with the splicing regulator p32.J Virol. 2006 Apr;80(7):3189-204. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.7.3189-3204.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16537587 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of p21(waf1) in human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1-infected cells and its association with cyclin A/cdk2.J Virol. 2000 Aug;74(16):7270-83. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.16.7270-7283.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10906181 Free PMC article.
-
The role of cyclin D2 and p21/waf1 in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 infected cells.Retrovirology. 2004 Apr 13;1:6. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-1-6. Retrovirology. 2004. PMID: 15169570 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathologic features of CDK6 translocation-associated B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders.Am J Surg Pathol. 2009 May;33(5):720-9. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181934244. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19145199 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Intrinsic Disorder and Phosphorylation by Oncogenic Viral Proteins to Dysregulate the Host Cell Cycle Through Interaction with pRb.Viruses. 2025 Jun 10;17(6):835. doi: 10.3390/v17060835. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40573426 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akagi T, Ono H, Shimotohno K. Expression of cell-cycle regulatory genes in HTLV-I infected T-cell lines: possible involvement of Tax1 in the altered expression of cyclin D2, p18Ink4 and p21Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1. Oncogene. 1996;12:1645–1652. - PubMed
-
- Arvanitakis L, Yaseen N, Sharma S. Latent membrane protein-1 induces cyclin D2 expression, pRb hyperphosphorylation, and loss of TGF-beta 1-mediated growth inhibition in EBV-positive B cells. J Immunol. 1995;155:1047–1056. - PubMed
-
- Bex F, Gaynor R B. Regulation of gene expression by HTLV-I Tax protein. Methods. 1998;16:83–94. - PubMed
-
- Blain S W, Montalvo E, Massague J. Differential interaction of the cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) inhibitor p27kip1 with cyclin A-Cdk2 and cyclin D2-Cdk4. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:25863–25872. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

