Altering the cellular location of an antigen expressed by a DNA-based vaccine modulates the immune response
- PMID: 10559338
- PMCID: PMC113075
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.12.10214-10223.1999
Altering the cellular location of an antigen expressed by a DNA-based vaccine modulates the immune response
Abstract
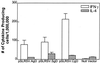
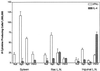
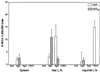
The potential for DNA vaccines encoding mutated versions of the same antigen to modulate immune responses in C3H/HeN mice was investigated. We created expression plasmids that encoded several versions of glycoprotein D (gD) from bovine herpesvirus 1, including authentic membrane-anchored glycoprotein (pSLRSV.AgD), a secreted glycoprotein (pSLRSV.SgD), and an intracellular protein (pSLRSV.CgD). Immunization of an inbred strain of mice with these plasmids resulted in highly efficacious and long-lasting humoral and cell-mediated immunity. We also demonstrated that the cell compartment in which plasmid-encoded gD was expressed caused a deviation in the serum immunoglobulin (Ig) isotype profile as well as the predominant cytokines secreted from the draining lymph node. Immunization of C3H/HeN mice with DNA vaccines encoding cell-associated forms of gD resulted in a predominance of serum IgG2a and gamma interferon-secreting cells within the spleens and draining lymph nodes. In contrast, mice immunized with a secreted form of this same antigen displayed immune responses characterized by greater levels of interleukin 4 in the draining lymph node and IgG1 as the predominant serum isotype. We also showed evidence of compartmentalization of distinct immune responses within different lymphoid organs.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Polynucleotide vaccines in animals: enhancing and modulating responses.Vaccine. 1997 Jun;15(8):861-4. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(96)00279-4. Vaccine. 1997. PMID: 9234534
-
Fusion of C3d molecule with bovine rotavirus VP7 or bovine herpesvirus type 1 glycoprotein D inhibits immune responses following DNA immunization.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2001 Nov;83(1-2):79-92. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(01)00369-5. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2001. PMID: 11604163
-
Induction of immune responses to bovine herpesvirus type 1 gD in passively immune mice after immunization with a DNA-based vaccine.J Gen Virol. 1999 Nov;80 ( Pt 11):2829-2837. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-80-11-2829. J Gen Virol. 1999. PMID: 10580044
-
Intradermal immunization with a bovine herpesvirus-1 DNA vaccine induces protective immunity in cattle.J Gen Virol. 1998 Apr;79 ( Pt 4):831-9. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-79-4-831. J Gen Virol. 1998. PMID: 9568979
-
DNA immunization with bovine herpesvirus-1 genes.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995 Nov 27;772:47-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1995.tb44731.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995. PMID: 8546413 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Nasal inoculation of an adenovirus vector encoding 11 tandem repeats of Abeta1-6 upregulates IL-10 expression and reduces amyloid load in a Mo/Hu APPswe PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Gene Med. 2007 Feb;9(2):88-98. doi: 10.1002/jgm.993. J Gene Med. 2007. PMID: 17219449 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of humoral responses to BHV-1 glycoprotein D expressed by HSV-1 amplicon vectors.J Vet Sci. 2012 Mar;13(1):59-65. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2012.13.1.59. J Vet Sci. 2012. PMID: 22437537 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of primary and secondary cellular immune responses against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gag by using DNA expression vectors that target Gag antigen to the secretory pathway.J Virol. 2000 Jul;74(13):5997-6005. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.13.5997-6005.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10846081 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal induction of T-cell responses against hepatitis C virus E2 by antigen engineering in DNA immunization.J Virol. 2003 Nov;77(21):11596-602. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.21.11596-11602.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 14557645 Free PMC article.
-
Develop an indirect ELISA utilizing gD protein to detect antibodies against bovine herpesvirus type 1.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 May 8;15:1591304. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1591304. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40406523 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aramaki Y, Suda H, Tsuchiya S. Interferon-inductive effect of liposomes as an immunoadjuvant. Vaccine. 1995;18:1809–1814. - PubMed
-
- Audibert F M, Lise L D. Adjuvants: current status, clinical perspectives, and future prospects. Immunol Today. 1993;14:281–284. - PubMed
-
- Babiuk L A, L’Italien J, van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S, Zamb T, Lawman M J P, Hughes G, Gifford G A. Protection of cattle from bovine herpesvirus type I (BHV-1) infection by immunization with individual viral glycoproteins. Virology. 1987;159:57–66. - PubMed
-
- Baca-Estrada M E, Snider M, Tikoo S K, Harland R, Babiuk L A, van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S. Immunogenicity of bovine herpesvirus-1 glycoprotein D in mice: effect of antigen form on the induction of cellular and humoral immune responses. Viral Immunol. 1996;9:11–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

