Increased induction of osteopetrosis, but unaltered lymphomagenicity, by murine leukemia virus SL3-3 after mutation of a nuclear factor 1 site in the enhancer
- PMID: 10559359
- PMCID: PMC113096
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.12.10406-10415.1999
Increased induction of osteopetrosis, but unaltered lymphomagenicity, by murine leukemia virus SL3-3 after mutation of a nuclear factor 1 site in the enhancer
Abstract
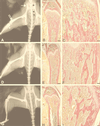
SL3-3 is a murine leukemia virus which is only weakly bone pathogenic but highly T-cell lymphomagenic. A major pathogenic determinant is the transcriptional enhancer comprising several transcription factor binding sites, among which are three identical sites for nuclear factor 1 (NF1). We have investigated the pathogenic properties of NF1 site enhancer mutants of SL3-3. Two different mutants carrying a 3-bp mutation either in all three NF1 sites or in the central site alone were constructed and assayed in inbred NMRI mice. The wild type and both mutants induced lymphomas in all mice, with a mean latency period of 9 weeks. However, there was a considerable difference in osteopetrosis induction. Wild-type SL3-3 induced osteopetrosis in 11% of the mice (2 of 19), and the triple NF1 site mutant induced osteopetrosis in none of the mice (0 of 19), whereas the single NF1 site mutant induced osteopetrosis in 56% (10 of 18) of the mice, as determined by X-ray analysis. A detailed histological examination of the femurs of the mice was carried out and found to support this diagnosis. Thus, the NF1 sites of SL3-3 are major determinants of osteopetrosis induction, without determining lymphomagenesis. This conclusion was further supported by evaluation of the bone pathogenicity of other SL3-3 enhancer variants, the lymphomagenicity of which had been examined previously. This evaluation furthermore strongly indicated that the core sites, a second group of transcription factor binding sites in the viral enhancer, are necessary for the osteopetrosis induction potential of SL3-3.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Increased lymphomagenicity and restored disease specificity of AML1 site (core) mutant SL3-3 murine leukemia virus by a second-site enhancer variant evolved in vivo.J Virol. 1997 Oct;71(10):7273-80. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.10.7273-7280.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9311802 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct roles of enhancer nuclear factor 1 (NF1) sites in plasmacytoma and osteopetrosis induction by Akv1-99 murine leukemia virus.Virology. 2005 Apr 10;334(2):234-44. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2005.01.039. Virology. 2005. PMID: 15780873
-
Stability of AML1 (core) site enhancer mutations in T lymphomas induced by attenuated SL3-3 murine leukemia virus mutants.J Virol. 1997 Jul;71(7):5080-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.7.5080-5087.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9188573 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of reversions and suppressors of a mutation in the CBF binding site of a lymphomagenic retrovirus.J Virol. 1999 Sep;73(9):7599-606. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.9.7599-7606.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 10438850 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analysis and characterization of two myeloid leukemia inducing murine retroviruses.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1996;211:201-10. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-85232-9_20. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8585951 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
RANKL-RANK signaling regulates expression of xenotropic and polytropic virus receptor (XPR1) in osteoclasts.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Aug 20;399(2):129-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.07.022. Epub 2010 Jul 13. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20633538 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of hematopoiesis and thymopoiesis in the early premalignant stages of infection with SL3-3 murine leukemia virus.J Virol. 2002 Mar;76(5):2363-74. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.5.2363-2374.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11836414 Free PMC article.
-
Control of pathogenicity and disease specificity of a T-lymphomagenic gammaretrovirus by E-box motifs but not by an overlapping glucocorticoid response element.J Virol. 2009 Jan;83(1):336-46. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01368-08. Epub 2008 Oct 22. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 18945767 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel Bach2 transcripts and protein isoforms through tagging analysis of retroviral integrations in B-cell lymphomas.BMC Mol Biol. 2009 Jan 21;10:2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-10-2. BMC Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19159451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams A, Choate D, Thompson M. NF1-L is the DNA-binding component of the protein complex at the peripherin negative regulatory element. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:6975–6983. - PubMed
-
- Alevizopoulos A, Dusserre Y, Tsai P M, van de Weid T, Wahli W, Mermod N. A proline-rich TGF-beta-responsive transcriptional activator interacts with histone H3. Genes Dev. 1995;9:3051–3066. - PubMed
-
- Beato M, Herrlich P, Schutz G. Steroid hormone receptors: many actors in search of a plot. Cell. 1995;83:851–857. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

