Total number and ratio of excitatory and inhibitory synapses converging onto single interneurons of different types in the CA1 area of the rat hippocampus
- PMID: 10559416
- PMCID: PMC6782984
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-22-10082.1999
Total number and ratio of excitatory and inhibitory synapses converging onto single interneurons of different types in the CA1 area of the rat hippocampus
Abstract
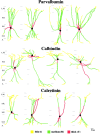
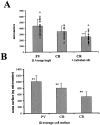
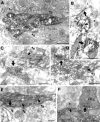
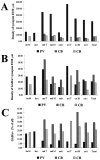
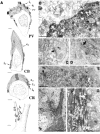
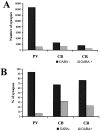
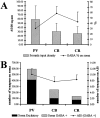
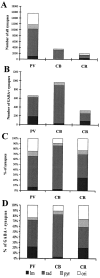
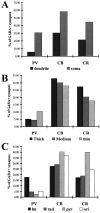
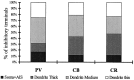
The least known aspect of the functional architecture of hippocampal microcircuits is the quantitative distribution of synaptic inputs of identified cell classes. The complete dendritic trees of functionally distinct interneuron types containing parvalbumin (PV), calbindin D(28k) (CB), or calretinin (CR) were reconstructed at the light microscopic level to describe their geometry, total length, and laminar distribution. Serial electron microscopic reconstruction and postembedding GABA immunostaining was then used to determine the density of GABA-negative asymmetrical (excitatory) and GABA-positive symmetrical (inhibitory) synaptic inputs on their dendrites, somata, and axon initial segments. The total convergence and the distribution of excitatory and inhibitory inputs were then calculated using the light and electron microscopic data sets. The three populations showed characteristic differences in dendritic morphology and in the density and distribution of afferent synapses. PV cells possessed the most extensive dendritic tree (4300 microm) and the thickest dendrites. CR cells had the smallest dendritic tree (2500 microm) and the thinnest shafts. The density of inputs as well as the total number of excitatory plus inhibitory synapses was several times higher on PV cells (on average, 16,294) than on CB (3839) or CR (2186) cells. The ratio of GABAergic inputs was significantly higher on CB (29.4%) and CR (20.71%) cells than on PV cells (6.4%). The density of inhibitory terminals was higher in the perisomatic region than on the distal dendrites. These anatomical data are essential to understand the distinct behavior and role of these interneuron types during hippocampal activity patterns and represent fundamental information for modeling studies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pyramidal cell dendrites are the primary targets of calbindin D28k-immunoreactive interneurons in the hippocampus.Hippocampus. 1996;6(5):525-34. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1063(1996)6:5<525::AID-HIPO5>3.0.CO;2-H. Hippocampus. 1996. PMID: 8953305
-
Total number and distribution of inhibitory and excitatory synapses on hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells.Neuroscience. 2001;102(3):527-40. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(00)00496-6. Neuroscience. 2001. PMID: 11226691
-
Convergence of excitatory and inhibitory inputs onto CCK-containing basket cells in the CA1 area of the rat hippocampus.Eur J Neurosci. 2004 Mar;19(5):1243-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03225.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15016082
-
GABAergic interneurons targeting dendrites of pyramidal cells in the CA1 area of the hippocampus.Eur J Neurosci. 2009 Sep;30(6):947-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06913.x. Epub 2009 Sep 4. Eur J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19735288 Review.
-
Neocortical inhibitory system.Folia Biol (Praha). 2009;55(6):201-17. Folia Biol (Praha). 2009. PMID: 20163769 Review.
Cited by
-
Common Principles in Functional Organization of VIP/Calretinin Cell-Driven Disinhibitory Circuits Across Cortical Areas.Front Neural Circuits. 2020 Jun 9;14:32. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2020.00032. eCollection 2020. Front Neural Circuits. 2020. PMID: 32581726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age-independent synaptogenesis by phosphoinositide 3 kinase.J Neurosci. 2006 Oct 4;26(40):10199-208. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1223-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17021175 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroligin 2 is expressed in synapses established by cholinergic cells in the mouse brain.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 5;8(9):e72450. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072450. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24039767 Free PMC article.
-
Interneuron Types and Their Circuits in the Basolateral Amygdala.Front Neural Circuits. 2021 Jun 10;15:687257. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2021.687257. eCollection 2021. Front Neural Circuits. 2021. PMID: 34177472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The glutamatergic synapse: a complex machinery for information processing.Cogn Neurodyn. 2021 Oct;15(5):757-781. doi: 10.1007/s11571-021-09679-w. Epub 2021 May 7. Cogn Neurodyn. 2021. PMID: 34603541 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Acsady L, Gorcs TJ, Freund TF. Different populations of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-immunoreactive interneurons are specialized to control pyramidal cells or interneurons in the hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1996;73:317–334. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG, Witter MP. The three-dimensional organization of the hippocampal formation: a review of anatomical data. Neuroscience. 1989;31:571–591. - PubMed
-
- Baimbridge KG, Miller JJ. Immunohistochemical localization of calcium-binding protein in the cerebellum, hippocampal formation and olfactory bulb of the rat. Brain Res. 1982;245:223–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
