Expression of alpha(1b) adrenoceptor mRNA in corticotropin-releasing hormone-containing cells of the rat hypothalamus and its regulation by corticosterone
- PMID: 10559417
- PMCID: PMC6782978
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-22-10098.1999
Expression of alpha(1b) adrenoceptor mRNA in corticotropin-releasing hormone-containing cells of the rat hypothalamus and its regulation by corticosterone
Abstract
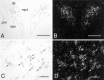
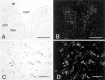
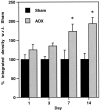
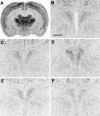
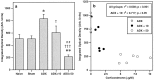
Considerable evidence supports a role for brainstem adrenergic and noradrenergic inputs to corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) cells of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN), in the control of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical (HPA) axis function. However, little is known about specific adrenoceptor (ADR) subtypes in CRH-containing cells of the PVN. Here we demonstrate, using dual in situ hybridization, that mRNA encoding alpha(1b) ADR is colocalized with CRH in the rat PVN. Furthermore, we confirm that these alpha(1b) ADR mRNA-containing cells are stress-responsive, by colocalization with c-fos mRNA after restraint, swim, or immune stress. To determine whether expression of alpha(1b) ADR mRNA is influenced by circulating glucocorticoids, male rats underwent bilateral adrenalectomy (ADX) or sham surgery, and were killed after 1, 3, 7, or 14 d. In situ hybridization revealed levels of alpha(1b) ADR mRNA were increased in the PVN 7 and 14 d after ADX, but were not altered in the hippocampus, amygdala, or dorsal raphe. Additional rats underwent ADX or sham surgery and received a corticosterone pellet (10 or 50 mg) or placebo for 7 d. Corticosterone replacement (10 mg) reduced the ADX-induced increase in PVN alpha(1b) ADR mRNA to control levels, whereas 50 mg of corticosterone replacement resulted in a decrease in PVN alpha(1b) ADR mRNA as compared with all other groups. Furthermore, levels of plasma corticosterone were significantly correlated (inverse relationship) with alpha(1b) ADR mRNA in the PVN. We conclude that alpha(1b) ADR mRNA is expressed in CRH-containing, stress-responsive cells of the PVN and is highly sensitive to circulating levels of corticosterone. Because activation of the alpha(1B) adrenoceptor is predominantly excitatory within the brain, we predict that this receptor plays an important role in facilitation of the HPA axis response.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased expression of corticotropin-releasing hormone and vasopressin messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus during repeated stress: association with reduction in glucocorticoid receptor mRNA levels.Endocrinology. 1995 Aug;136(8):3299-309. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.8.7628364. Endocrinology. 1995. PMID: 7628364
-
Evidence that elevated plasma corticosterone levels are the cause of reduced hypothalamic corticotrophin-releasing hormone gene expression in diabetes.Regul Pept. 1997 Oct 31;72(2-3):105-12. doi: 10.1016/s0167-0115(97)01043-4. Regul Pept. 1997. PMID: 9652969
-
Regulation of corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor messenger ribonucleic acid in the rat brain and pituitary by glucocorticoids and stress.Endocrinology. 1995 Oct;136(10):4517-25. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.10.7664672. Endocrinology. 1995. PMID: 7664672
-
Stress Adaptation and the Brainstem with Focus on Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 23;22(16):9090. doi: 10.3390/ijms22169090. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation of corticotropin-releasing hormone gene in stress response.IBRO Rep. 2018 Aug 23;5:137-146. doi: 10.1016/j.ibror.2018.08.003. eCollection 2018 Dec. IBRO Rep. 2018. PMID: 30591954 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HPA axis responsiveness to stress: implications for healthy aging.Exp Gerontol. 2011 Feb-Mar;46(2-3):90-5. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2010.08.023. Epub 2010 Sep 9. Exp Gerontol. 2011. PMID: 20833240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic stress-induced neurotransmitter plasticity in the PVN.J Comp Neurol. 2009 Nov 10;517(2):156-65. doi: 10.1002/cne.22142. J Comp Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19731312 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of hippocampal alpha1d adrenergic receptor mRNA by corticosterone in adrenalectomized rats.Brain Res. 2008 Jul 7;1218:132-40. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.04.067. Epub 2008 May 1. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18534559 Free PMC article.
-
Brain stem catecholamines circuitry: activation by alcohol and role in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal response to this drug.J Neuroendocrinol. 2011 Jun;23(6):531-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2011.02131.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21447066 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and its modulation by glucocorticoids and stress.Front Cell Neurosci. 2012 May 11;6:24. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2012.00024. eCollection 2012. Front Cell Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22593735 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akil H, Campeau S, Cullinan WE, Lechan RM, Toni R, Watson SJ, Moore RY. Neuroendocrine systems I: overview–thyroid and adrenal axes. In: Zigmond M, Bloom F, Landis S, Roberts J, Squire L, editors. Fundamental neuroscience. Academic; San Diego: 1999. pp. 1127–1150.
-
- Cullinan WE, Herman JP, Battaglia DF, Akil H, Watson SJ. Pattern and time course of immediate early gene expression in rat brain following acute stress. Neuroscience. 1995;64:477–505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
