Protein tyrosine phosphatase alpha (PTPalpha) and contactin form a novel neuronal receptor complex linked to the intracellular tyrosine kinase fyn
- PMID: 10562275
- PMCID: PMC2156155
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.147.4.707
Protein tyrosine phosphatase alpha (PTPalpha) and contactin form a novel neuronal receptor complex linked to the intracellular tyrosine kinase fyn
Abstract
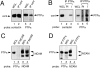
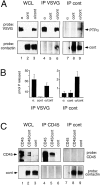
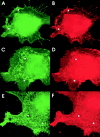
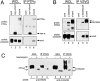
Glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked receptors and receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases (RPTPs), both play key roles in nervous system development, although the molecular mechanisms are largely unknown. Despite lacking a transmembrane domain, GPI receptors can recruit intracellular src family tyrosine kinases to receptor complexes. Few ligands for the extracellular regions of RPTPs are known, relegating most to the status of orphan receptors. We demonstrate that PTPalpha, an RPTP that dephosphorylates and activates src family kinases, forms a novel membrane-spanning complex with the neuronal GPI-anchored receptor contactin. PTPalpha and contactin associate in a lateral (cis) complex mediated through the extracellular region of PTPalpha. This complex is stable to isolation from brain lysates or transfected cells through immunoprecipitation and to antibody-induced coclustering of PTPalpha and contactin within cells. This is the first demonstration of a receptor PTP in a cis configuration with another cell surface receptor, suggesting an additional mode for regulation of a PTP. The transmembrane and catalytic nature of PTPalpha indicate that it likely forms the transducing element of the complex, and we postulate that the role of contactin is to assemble a phosphorylation-competent system at the cell surface, conferring a dynamic signal transduction capability to the recognition element.
Figures
References
-
- Beggs H.E., Baragona S.C., Hemperly J.J., Maness P.F. NCAM140 interacts with the focal adhesion kinase p125fak and the SRC related tyrosine kinase p59fyn . J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:8310–8319 . - PubMed
-
- Bhandari V., Lim K.L., Pallen C.J. Physical and functional interactions between receptor-like protein-tyrosine phosphatase α and p59fyn . J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:8691–8698 . - PubMed
-
- Brümmendorf T., Wolff J.M., Frank R., Rathjen F.G. Neural cell recognition molecule F11homology with fibronectin type III and immunoglobulin type C domains. Neuron. 1989;2:1351–1361 . - PubMed
-
- Brümmendorf T., Hubert M., Treubert U., Leuschner R., Tàrnok A., Rathjen F.G. The axonal recognition molecule F11 is a multifunctional proteinspecific domains mediate interactions with Ng-CAM and restrictin. Neuron. 1993;10:711–727 . - PubMed
-
- Buj-Bello A., Adu J., Pinon L.G.P., Horton A., Thompson J., Rosenthal A., Chinchetru M., Buchman V.L., Davies A.M. Neurturin responsiveness requires a GPI-linked receptor and the Ret receptor tyrosine kinase. Nature. 1997;387:721–724 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

