PEX12 interacts with PEX5 and PEX10 and acts downstream of receptor docking in peroxisomal matrix protein import
- PMID: 10562279
- PMCID: PMC2156163
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.147.4.761
PEX12 interacts with PEX5 and PEX10 and acts downstream of receptor docking in peroxisomal matrix protein import
Abstract
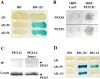
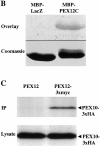
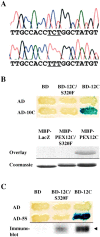
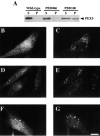
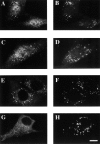
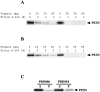
Peroxisomal matrix protein import requires PEX12, an integral peroxisomal membrane protein with a zinc ring domain at its carboxy terminus. Mutations in human PEX12 result in Zellweger syndrome, a lethal neurological disorder, and implicate the zinc ring domain in PEX12 function. Using two-hybrid studies, blot overlay assays, and coimmunoprecipitation experiments, we observed that the zinc-binding domain of PEX12 binds both PEX5, the PTS1 receptor, and PEX10, another integral peroxisomal membrane protein required for peroxisomal matrix protein import. Furthermore, we identified a patient with a missense mutation in the PEX12 zinc-binding domain, S320F, and observed that this mutation reduces the binding of PEX12 to PEX5 and PEX10. Overexpression of either PEX5 or PEX10 can suppress this PEX12 mutation, providing genetic evidence that these interactions are biologically relevant. PEX5 is a predominantly cytoplasmic protein and previous PEX5-binding proteins have been implicated in docking PEX5 to the peroxisome surface. However, we find that loss of PEX12 or PEX10 does not reduce the association of PEX5 with peroxisomes, demonstrating that these peroxins are not required for receptor docking. These and other results lead us to propose that PEX12 and PEX10 play direct roles in peroxisomal matrix protein import downstream of the receptor docking event.
Figures



References
-
- Adams A., Gottschling D.E., Kaiser C.A., Stearns T. Methods in Yeast Genetics 1997. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor: pp. 115–116
-
- Albertini M., Rehling P., Erdmann R., Girzalsky W., Kiel J.A., Veenhuis M., Kunau W.-H. Pex14p, a peroxisomal membrane protein binding both receptors of the two PTS-dependent import pathways. Cell. 1997;89:83–92 . - PubMed
-
- Baes M., Gressens P., Baumgart E., Carmeliet P., Casteels M., Fransen M., Evrard P., Fahimi D., Declercq P.E., Collen D., van Veldhoven P.P., Mannaerts G.P. A mouse model for Zellweger syndrome. Nat. Genet. 1997;17:49–57 . - PubMed
-
- Borden K.L. RING fingers and B-boxeszinc-binding protein-protein interaction domains. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1998;76:351–358 . - PubMed
-
- Braverman N., Dodt G., Gould S.J., Valle D. Disorders of peroxisome biogenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1995;4:1791–1798 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

